In the intricate dance of human biology, hormones play a pivotal role, influencing everything from mood and energy levels to physical health and well-being. Among these, testosterone stands out as a key player, particularly in the lives of men, where it is often associated with vitality, strength, and masculinity. However, as awareness around testosterone therapy has grown, so too have the questions surrounding its safety and efficacy. Is this treatment a beacon of hope for those grappling with low testosterone levels, or does it carry risks that warrant caution? This article delves into the nuances of testosterone therapy, exploring the latest research, potential benefits, and safety concerns to provide a comprehensive understanding of this controversial subject. Whether you are considering therapy for yourself or simply seeking to understand the conversation, join us as we unravel the complexities of testosterone and its role in health and wellness.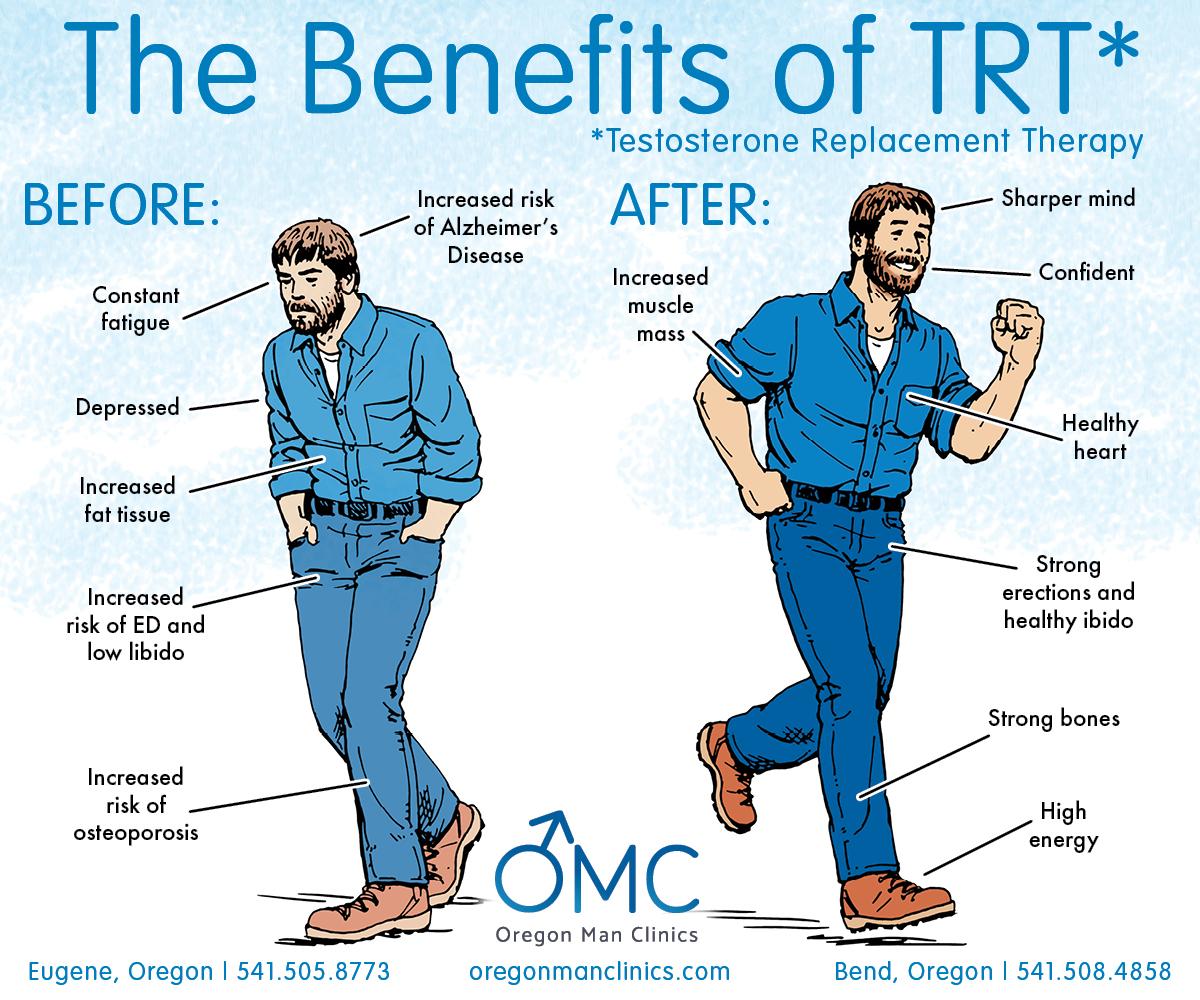
Understanding Testosterone Therapy and Its Purpose
Testosterone therapy is primarily utilized to address deficiencies in testosterone levels, particularly in men experiencing symptoms associated with low testosterone, often referred to as “low T.” This therapy can be delivered in various forms, including injections, gels, patches, and pellets, which aim to restore hormonal balance and improve quality of life. Common reasons for initiating treatment include fatigue, decreased libido, muscle loss, and mood disturbances. However, it’s essential to determine the underlying cause of low testosterone before commencing therapy, as factors such as age, lifestyle, and overall health can significantly influence testosterone levels.
While testosterone therapy can offer substantial benefits, such as increased energy, enhanced mood, and improved sexual function, it is not devoid of potential risks and side effects. Patients should be well-informed about both the positives and negatives associated with treatment. Some possible side effects include:
- Acne
- Sleep apnea
- Increased risk of blood clots
- Prostate enlargement or cancer
A healthcare professional can assess individual risk factors and monitor for potential complications throughout the therapy process. It’s vital for individuals considering testosterone therapy to engage in open discussions with their doctor, weighing the possible advantages against the risks involved.
The Benefits of Testosterone Therapy for Men and Women
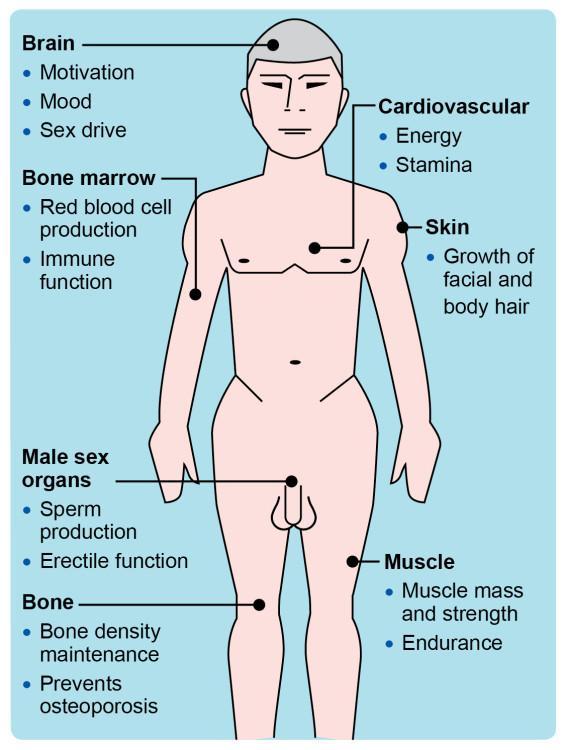
Testosterone therapy has gained recognition for its ability to enhance quality of life in both men and women. This treatment helps address hormonal imbalances, leading to several potential benefits that go beyond mere physical changes. Individuals undergoing testosterone therapy often report improvements in mood, with reduced feelings of anxiety and depression. This therapy can also bolster energy levels and enhance overall vitality, allowing for a more active and engaged lifestyle. Additional advantages include:
- Increased muscle mass and strength: Hormonal therapy can aid in muscle development and combat age-related muscle loss.
- Improved libido: Many patients experience a resurgence in sexual desire and performance.
- Enhanced cognitive function: Improved focus, memory, and concentration are often noted.
Moreover, the impact of testosterone therapy on bone density is significant. As testosterone plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health, therapy can reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, especially in older adults. Some studies also suggest a correlation between appropriate testosterone levels and a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases. Here’s a concise summary of the key benefits:
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Muscle Strength | Supports muscle mass development and maintenance. |
| Mood Enhancement | Addresses anxiety and depression symptoms. |
| Sexual Health | Increases libido and performance in intimate relations. |
| Bone Density | Strengthens bones and reduces the risk of fractures. |
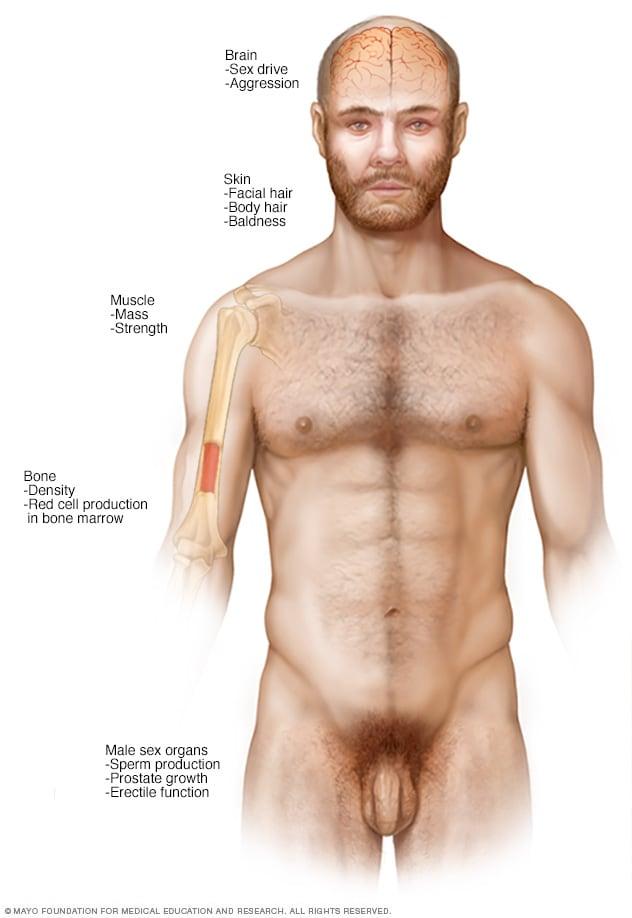
Assessing Risks and Side Effects Associated with Treatment
When considering testosterone therapy, it is vital to evaluate the potential risks and side effects that may accompany treatment. Though many individuals experience positive outcomes, it is important to remember that not everyone responds similarly. Commonly reported side effects of testosterone therapy may include:
- Acne – Individuals may notice an increase in skin oiliness
- Sleep Apnea - A worsening or new onset of sleep disturbances can occur
- Hair Loss – Some may experience increased hair thinning
- Breast Enlargement – Gynecomastia is a possibility in some cases
- Fluid Retention – Increased retention can lead to swelling
In addition to these side effects, there are also significant risks that need to be addressed. For some individuals, testosterone therapy can elevate the risk of cardiovascular issues. It is particularly essential to be aware of:
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Heart Attack | Potentially increased incidence among older men |
| Stroke | Possible higher risk with prolonged use |
| Prostate Issues | May exacerbate existing conditions or increase size |
Each individual’s health history and risk factors should be thoroughly evaluated to make informed decisions regarding testosterone therapy. Regular monitoring and consultations with healthcare professionals are strongly recommended to mitigate potential consequences and ensure safe treatment practices.
Identifying Candidates for Testosterone Therapy
Determining whether a patient is a suitable candidate for testosterone therapy involves a thorough evaluation of their medical history, symptoms, and overall health. Key factors to consider include:
- Age: While testosterone levels naturally decline with age, it’s crucial to assess whether symptoms correlate directly with low testosterone.
- Symptoms: Look for common signs such as fatigue, weight gain, depression, decreased libido, and reduced muscle mass, which may indicate hormonal imbalances.
- Medical Conditions: Assess for existing conditions like obesity, diabetes, sleep apnea, and prostate health issues that could affect therapy suitability.
Before initiating therapy, physicians often recommend conducting comprehensive blood tests to confirm low testosterone levels. These tests typically involve measuring testosterone in the morning when levels peak. Here’s a simple overview of common testing protocols:
| Test Type | Purpose | Typical Timing |
|---|---|---|
| Total Testosterone | Assess overall testosterone levels | One morning sample |
| Free Testosterone | Evaluate bioavailable testosterone | One morning sample |
| SHBG | Measure binding hormone levels | Concurrent with testosterone testing |
Monitoring and Managing Therapy Effectiveness
Monitoring the effectiveness of testosterone therapy involves regular assessments to ensure that the treatment is providing the desired benefits while minimizing potential risks. This includes periodic blood tests to measure testosterone levels, as well as evaluating the patient’s overall health and well-being. Key indicators to observe include:
- Energy Levels: Noticing improvements in fatigue or lethargy can signal that therapy is working.
- Mood Changes: An increase in mood stability or reduction in depressive symptoms may be a positive sign of hormonal balance.
- Physical Changes: Changes in muscle mass, fat distribution, and libido can all serve as indicators to monitor.
Alongside physical assessments, managing therapy effectiveness entails being vigilant about any adverse effects that may arise. Patients should be encouraged to report any unusual symptoms, such as headaches, sleep apnea, or cardiovascular changes. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals are critical. These visits can help assess:
| Follow-Up Aspect | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Blood Tests for Testosterone Levels | Every 3-6 months |
| Mental Health Evaluations | Every 6-12 months |
| Cardiovascular Risk Assessments | Annual or as needed |
By maintaining open lines of communication and scheduling regular evaluations, patients and healthcare providers can collaboratively ensure that testosterone therapy remains both effective and safe.
Navigating Regulatory Guidelines and Best Practices
When considering testosterone therapy, it is essential to be aware of the regulatory frameworks that govern its use. Various organizations, including the Endocrine Society and the American Urological Association, provide guidelines that healthcare professionals should follow to ensure patient safety and efficacy of treatment. Practitioners must conduct a thorough assessment before initiating therapy, including:
- Comprehensive medical history review
- Physical examination
- Laboratory testing, including testosterone levels
In addition to clinical assessments, healthcare providers should remain updated on local and federal regulations surrounding the prescription of testosterone. Adherence to best practices involves regular monitoring of patients throughout the duration of therapy. This includes assessing:
- Testosterone levels
- Hematocrit levels to prevent polycythemia
- Cardiovascular health and potential risks
| Monitoring Parameter | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Testosterone Levels | Every 3-6 months |
| Hematocrit Levels | Every 6-12 months |
| Cardiovascular Assessment | Annually |
Making Informed Decisions: Consulting Healthcare Professionals
When considering testosterone therapy, it is crucial to engage with healthcare professionals who are well-versed in hormonal treatments. Consulting with a specialist, such as an endocrinologist or a urologist, can provide valuable insights tailored to individual health profiles. These professionals can evaluate symptoms and conduct tests to determine necessary hormone levels. Engaging in open discussions allows patients to ask pertinent questions and address concerns about potential risks, benefits, and alternative treatment options. This collaborative approach ensures that decisions about testosterone therapy are made based on comprehensive clinical evaluations rather than assumptions or anecdotal experiences.
Moreover, reputable healthcare professionals will often utilize evidence-based guidelines to inform their recommendations. To better understand the patient’s unique situation, they may review personal medical history, age, and lifestyle factors. Here are some critical considerations they might focus on during consultations:
- Symptoms assessment: Understanding the specific symptoms prompting consideration of therapy.
- Comorbidity evaluation: Identifying pre-existing health conditions that could influence therapy safety.
- Possible side effects: Discussing known risks, including cardiovascular effects or mood changes.
Utilizing a structured approach can provide clarity and confidence in making health-related choices. Here’s a simplified comparison of potential benefits and risks associated with testosterone therapy:
| Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|
| Increased energy levels | Potential for heart complications |
| Improved mood | Risk of sleep apnea |
| Enhanced sexual function | Acne and skin irritations |
Q&A
Q&A: Is Testosterone Therapy Safe?
Q1: What is testosterone therapy?
A: Testosterone therapy involves the administration of testosterone to individuals with low levels of the hormone. It can be delivered through injections, patches, gels, or pellets, and is often pursued by men experiencing symptoms of low testosterone, such as fatigue, depression, and reduced libido.
Q2: Who might need testosterone therapy?
A: Typically, testosterone therapy is considered for men diagnosed with hypogonadism, a condition characterized by insufficient natural testosterone production. However, some may seek therapy for symptoms commonly associated with aging or other conditions. It’s essential for individuals to consult healthcare providers for appropriate evaluation and diagnosis.
Q3: What are the potential benefits of testosterone therapy?
A: Many people report improvements in energy levels, mood, muscle mass, bone density, and sexual function after beginning testosterone therapy. Some studies have suggested potential cognitive benefits and improved quality of life. Nonetheless, these effects can vary significantly among individuals.
Q4: What are the risks associated with testosterone therapy?
A: Risks may include increased levels of red blood cells, which can lead to blood clots; worsening of sleep apnea; fluid retention; and potential impacts on cardiovascular health. There have been debates about a possible link between testosterone therapy and heart issues, so understanding personal health status is crucial.
Q5: Is testosterone therapy safe for older adults?
A: The safety of testosterone therapy in older adults is a subject of ongoing research. While some older men may benefit from treatment, others may experience heightened risk factors for cardiovascular problems. Discussions with healthcare providers about personalized risks and benefits are essential for older populations considering therapy.
Q6: How can individuals determine if testosterone therapy is right for them?
A: Individuals should start with a complete evaluation by a healthcare professional, including a discussion of symptoms and relevant blood tests to measure testosterone levels. A thorough medical history and an assessment of risks versus benefits can guide whether therapy is a suitable choice.
Q7: What should one consider before starting testosterone therapy?
A: Before starting therapy, it’s important to discuss all medical history, potential risks, benefits, and alternative treatment options with a healthcare provider. Regular monitoring after beginning therapy is crucial to adjust the dose as necessary and observe any side effects.
Q8: Are there natural ways to boost testosterone?
A: Indeed! Lifestyle changes can help naturally boost testosterone levels. Engaging in regular exercise, focusing on strength training, maintaining a healthy diet rich in whole foods, ensuring adequate sleep, and managing stress levels can all contribute positively to hormonal balance.
Q9: Is it advisable to self-prescribe testosterone therapy?
A: No, self-prescribing testosterone is not advisable. Hormone therapy should only be undertaken under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional to ensure safety, proper diagnosis, and tailored treatment. Unsupervised use can lead to serious health risks and complications.
Q10: Where can readers find more reliable information on testosterone therapy?
A: Readers are encouraged to consult healthcare providers for personalized advice, as well as reputable medical organizations such as the Endocrine Society and the American Urological Association. These sources provide comprehensive insights and guidelines on hormone therapy and related health concerns.
This Q&A aims to provide a thoughtful and balanced exploration of testosterone therapy, empowering readers to engage actively with their health decisions.
In Retrospect
the conversation surrounding testosterone therapy is anything but black and white. As we navigate through the myriad studies, opinions, and patient experiences, one thing becomes clear: safety is a multifaceted concept that requires careful consideration. For some, testosterone therapy may offer a pathway to enhanced well-being and vitality, while for others, the potential risks might outweigh the benefits.
As research continues to evolve, it’s essential for individuals to engage in open dialogue with healthcare professionals, weighing personal health profiles against current scientific insights. Just as each individual is unique, so too are the responses to treatment—making personalized care paramount in the decision-making process.
Ultimately, whether you stand on the fringe or are deeply entrenched in this debate, the key takeaway remains the same: informed choices pave the way for empowered health journeys. As we move forward in understanding the implications of testosterone therapy, let us do so with curiosity, caution, and a commitment to prioritizing well-being above all else.










