In the intricate landscape of human health, few substances wield as significant an influence as testosterone. Often celebrated for its role in physical vitality and vigor, this hormone’s enigmatic connection to brain health remains a topic of growing interest and investigation. As scientific research unravels the complexities of testosterone therapy, a new narrative emerges—not just one of enhancement in muscle mass or libido, but of potential cognitive benefits and mental resilience. This article delves into the evolving discourse surrounding testosterone therapy and its implications for brain health, examining the latest findings, addressing common misconceptions, and exploring the delicate balance between hormonal levels and cognitive function in both men and women. With an eye toward understanding the role of testosterone in a holistic approach to wellness, we embark on a journey to uncover how this powerful hormone shapes not just our bodies but also the intricate workings of our minds.
The Role of Testosterone in Cognitive Function and Mood Regulation
Testosterone plays a multifaceted role in cognitive function and mood regulation, influencing various brain processes that contribute to our overall mental health. Research indicates that adequate levels of testosterone correlate positively with enhanced memory, learning capabilities, and spatial awareness. Specifically, this hormone appears to facilitate neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity, two critical processes for maintaining optimal cognitive performance as we age. Furthermore, testosterone may help modulate neurotransmitter systems, thus impacting mood stability and the risk of mood disorders.
The effects of testosterone on mood can be particularly pronounced, offering a potential pathway for therapeutic interventions in individuals experiencing mood dysregulation or cognitive decline. Evidence suggests that optimal testosterone levels may:
- Enhance mood and reduce feelings of depression: Higher testosterone levels have been linked to lower rates of depression and anxiety.
- Support emotional resilience: Testosterone may bolster the brain’s response to stress, promoting better coping mechanisms.
- Improve focus and motivation: A balanced testosterone level can potentially increase motivation, leading to heightened cognitive engagement.
Understanding the nuanced interplay between testosterone and brain health underscores the potential benefits of testosterone therapy. Nevertheless, it’s essential to approach treatment with caution and consult healthcare professionals for assessments. Below is a table summarizing key effects of testosterone on cognitive and mood functions:
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Memory Enhancement | Improved short-term and long-term memory capabilities. |
| Mood Stabilization | Reduction in depressive symptoms and mood swings. |
| Cognitive Flexibility | Enhanced ability to adapt to changing environments and learn new information. |
Understanding the Relationship Between Hormonal Changes and Neurodegenerative Diseases
As research continues to unveil the intricate connections between hormonal fluctuations and neurodegenerative conditions, attention is increasingly drawn to the role of testosterone. Men typically experience a gradual decline in testosterone levels with age, a phenomenon known as andropause. This decrease has been associated with several cognitive issues, including memory impairments and mood changes. Emerging studies suggest that maintaining adequate testosterone levels may play a significant part in neuroprotection, potentially reducing the risk of diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Enhanced cognitive function and improved overall brain health could be a pivotal benefit of testosterone therapy, especially for older men experiencing symptoms related to low testosterone.
The effects of testosterone therapy on brain health are multi-faceted, and several mechanisms have been proposed to explain its potential benefits. These include:
- Neurogenesis: Testosterone may stimulate the birth of new neurons, thereby supporting cognitive functions.
- Reduced Inflammation: The therapy might alleviate neuroinflammation, a common contributor to neurodegenerative diseases.
- Improved Blood Flow: It has been suggested that testosterone aids in enhancing cerebral blood flow, crucial for optimal brain function.
While the promise of testosterone therapy is compelling, it remains essential to approach this treatment with caution. Monitoring and consultation with healthcare professionals are recommended to tailor approaches for individual needs, ensuring both efficacy and safety.
Examining the Impacts of Testosterone Therapy on Brain Plasticity
Recent research into the realm of testosterone therapy has illuminated its potential effects on brain plasticity, unveiling a complex interplay between hormonal balance and cognitive resilience. Testosterone is not only pivotal for physical health but also plays a significant role in enhancing neurotransmission and synaptic connectivity, leading to improvements in learning and memory. Studies suggest that the presence of testosterone can facilitate neurogenesis in regions such as the hippocampus, which is critical for memory formation and spatial navigation. This hormone appears to stimulate synaptic plasticity through the modulation of various neurotransmitter systems, including glutamate and GABA, which are essential for maintaining cognitive flexibility.
Moreover, understanding how testosterone levels fluctuate with age and lifestyle factors has broad implications for targeting cognitive decline in older adults. Research indicates that testosterone therapy may lead to enhanced cognitive functions in men with lower baseline levels, with benefits including improved attention, verbal memory, and executive functions. To further illustrate, the following table summarizes key findings on the impacts of testosterone therapy on cognitive functions:
| Study | Participants | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Smith et al. (2020) | 100 Men, aged 50+ | Increased verbal memory |
| Johnson & Lee (2021) | 80 Older Adults | Enhanced executive functions |
| Garcia et al. (2022) | 120 Men, aged 40-60 | Improved attention span |
This emerging evidence underscores the significance of testosterone in brain health, suggesting that targeted hormone therapy could serve as a viable intervention to bolster cognitive resilience as we age.
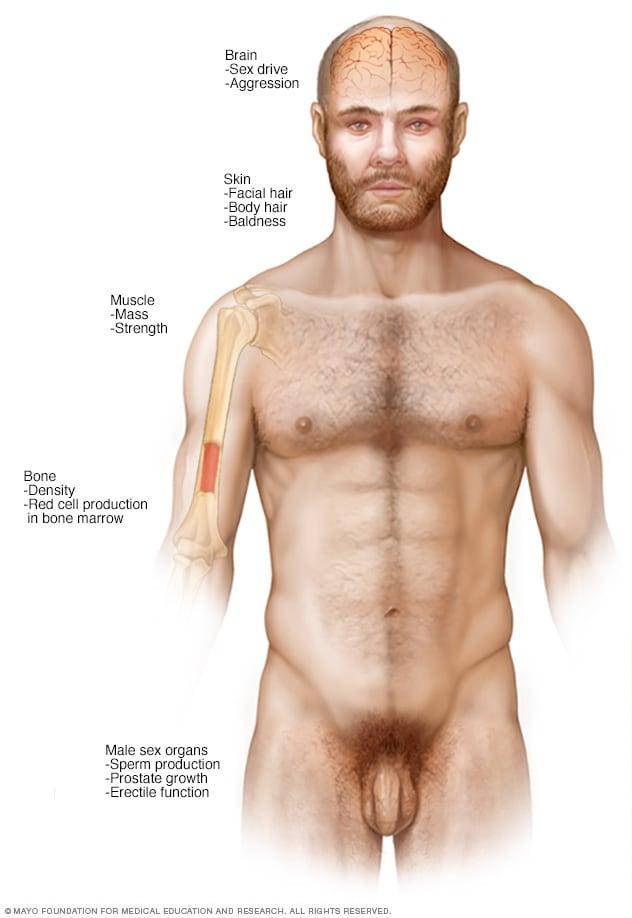
Benefits and Risks: Weighing the Evidence for Testosterone Therapy in Aging Adults
The decision to pursue testosterone therapy in aging adults involves a careful evaluation of both benefits and risks. On the one hand, testosterone therapy may offer several advantages, particularly concerning brain health. Research suggests that increased testosterone levels are associated with improvements in cognitive function, memory retention, and overall mental well-being. Additionally, it may contribute to enhanced mood, reduced feelings of anxiety and depression, and possibly lower the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. The following benefits have been noted:
- Improved Cognitive Function: Some studies indicate a correlation between testosterone and enhanced memory performance.
- Increased Energy Levels: Patients often report greater vitality and reduced fatigue.
- Better Mood Regulation: A boost in testosterone can play a crucial role in alleviating depressive symptoms.
Conversely, the pursuit of testosterone therapy is not without its potential drawbacks. Elevated testosterone levels have been linked to adverse effects, particularly in the aging demographic. Risks associated with the therapy may include cardiovascular issues, changes in mood stability, and potential impacts on prostate health. It is vital to consider the breadth of these risks, which can be summarized as follows:
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Issues | Higher testosterone may elevate the risk of heart disease. |
| Mood Instability | Some may experience increased irritability or aggression. |
| Prostate Health Concerns | Potential growth of prostate tissue, requiring careful monitoring. |
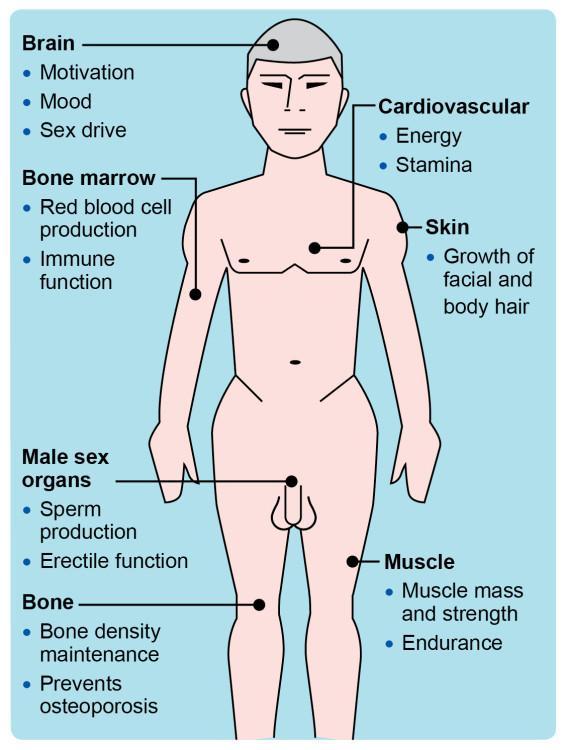
Practical Guidelines for Initiating and Monitoring Testosterone Treatment
When starting testosterone therapy, it’s essential to begin with a thorough assessment of the patient’s medical history, including any pre-existing conditions and medications that may interact with treatment. Consulting with a healthcare provider who specializes in hormonal therapies is crucial for tailoring the approach to individual needs. Key considerations include:
- Baseline hormonal levels: Obtain initial testosterone measurements to guide treatment decisions.
- Comorbidities: Evaluate any existing health issues, particularly those related to cardiovascular health, diabetes, or mental health.
- Informed consent: Ensure the patient understands the benefits and risks associated with testosterone therapy.
Once therapy is initiated, monitoring is vital to assess effectiveness and side effects. Regular follow-ups should include hormonal level checks and evaluations of any symptoms or changes in health. Important monitoring guidelines include:
- Testosterone levels: Reassess levels every 3 to 6 months during the first year of therapy.
- Health outcomes: Monitor for improvements in mood, cognitive function, and overall quality of life.
- Adverse effects: Be vigilant about potential side effects, such as increased aggression, mood swings, or changes in sleep patterns.
Lifestyle Factors That Enhance the Efficacy of Testosterone Therapy
Integrating certain lifestyle practices can significantly bolster the benefits derived from testosterone therapy. Nutrition plays a pivotal role; a diet rich in healthy fats, lean proteins, and an array of colorful fruits and vegetables can support hormone levels and overall well-being. Consider incorporating foods high in zinc and vitamin D, as they are essential for testosterone production. Additionally, staying hydrated and limiting sugar intake can prevent insulin spikes, which could otherwise disrupt hormonal balance. A well-rounded dietary approach not only enhances therapy outcomes but also promotes cognitive health, potentially mitigating the risk of neurodegenerative disorders.
Equally important are physical activity and sleep hygiene. Engaging in regular exercise, particularly resistance training and high-intensity interval training, not only boosts testosterone levels but also improves mood and cognitive function. Establishing a consistent sleep routine ensures adequate rest, allowing the body to recover and maintain optimal hormone levels. Stress management techniques, such as meditation and mindfulness, can further enhance the efficacy of testosterone therapy by reducing cortisol levels, which may otherwise inhibit testosterone’s benefits. Cultivating these lifestyle factors can create a synergistic effect, enriching both mental acuity and overall health.
Future Directions: Research Trends and Emerging Treatments in Hormonal Health
As research into hormonal health continues to evolve, the intersection of testosterone therapy and brain health presents a promising frontier. Emerging studies are focusing on the potential neuroprotective effects of testosterone, particularly in aging populations and those experiencing cognitive decline. Initial findings suggest that restoring optimal testosterone levels may not only enhance mood and energy but could also play a critical role in mitigating risks associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Accordingly, the scientific community is exploring various treatment protocols that could maximize these benefits while minimizing potential side effects.
To further understand the implications of testosterone on brain health, several key trends are emerging:
- Precision Medicine: Customizing testosterone therapy based on individual genetic makeup and hormonal profiles is becoming increasingly significant.
- Neuroimaging Techniques: Advances in brain imaging are helping researchers visualize the effects of testosterone on brain structure and function.
- Longitudinal Studies: Ongoing studies with extended timeframes aim to provide comprehensive insights into the long-term effects of testosterone therapy on cognitive health.
| Research Focus | Description |
|---|---|
| Neuroprotection | Understanding how testosterone may protect against neuronal loss. |
| Cognitive Enhancement | Assessing the impact of testosterone on memory and learning processes. |
| Quality of Life | Evaluating improvements in overall mental well-being post-therapy. |
Q&A
Q&A: Testosterone Therapy and Brain Health
Q1: What is testosterone therapy, and who typically undergoes it?
A: Testosterone therapy involves the administration of testosterone to individuals whose bodies do not produce enough of this hormone. Typically, men with low testosterone levels—often due to age, medical conditions, or certain lifestyle factors—consider this therapy. However, there’s ongoing research looking at its effects across various demographics, including women in specific medical contexts.
Q2: How does testosterone affect brain health?
A: Testosterone plays a role in various cognitive functions and mood regulation. Studies suggest that adequate levels of testosterone can support memory, increase cognitive flexibility, and enhance overall mood. Conversely, low testosterone may be linked to cognitive decline and increased feelings of depression or anxiety.
Q3: Are there any risks associated with testosterone therapy?
A: Yes, while testosterone therapy can benefit many, it is not without risks. Potential side effects include increased risk of cardiovascular events, sleep apnea, and mood changes. It’s essential for individuals considering therapy to discuss these risks with qualified healthcare professionals.
Q4: Can testosterone therapy help prevent age-related cognitive decline?
A: While some studies suggest that testosterone therapy may have a protective effect against cognitive decline, the evidence isn’t conclusive. More research is needed to determine the long-term impact of therapy on aging brains. It’s crucial to approach this subject with caution, weighing potential benefits against risks.
Q5: What should someone consider before starting testosterone therapy?
A: Before embarking on testosterone therapy, individuals should consult with healthcare providers to assess their hormonal levels, discuss symptoms, and evaluate their personal health history. Factors like age, existing health conditions, and any medications being taken should be carefully considered.
Q6: Are there alternative treatments for cognitive health aside from testosterone therapy?
A: Certainly! Cognitive health can be bolstered through various means, including regular physical exercise, a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, sufficient sleep, and engaging in mental challenges like puzzles or learning new skills. Lifestyle changes and holistic approaches might offer significant benefits alongside, or in place of, hormone therapy.
Q7: Is there a simple way to monitor testosterone levels in men?
A: Yes, monitoring testosterone levels typically involves a straightforward blood test. Healthcare providers may recommend testing in the morning when testosterone levels are at their peak. If levels are determined to be low, they may suggest further testing and discussions about possible therapy options.
Q8: What’s the current state of research in testosterone therapy and its link to brain health?
A: Research is actively ongoing, with studies exploring the complex relationship between testosterone, cognitive function, and mental health. While some findings are promising, the field is still evolving. Researchers are keen to determine optimal treatment protocols, long-term effects, and which populations may benefit most.
Q9: Are there specific populations at higher risk for low testosterone levels?
A: Yes, older men are typically at higher risk for low testosterone levels due to natural aging processes. Additionally, individuals with certain chronic illnesses, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and hormonal disorders may also be at higher risk. Understanding these factors can help lead to earlier detection and treatment.
Q10: What final advice would you give to someone considering testosterone therapy for brain health?
A: Knowledge is key. Equip yourself with information, consult healthcare experts, and weigh the pros and cons carefully. What works for one person might not work for another. Focus on overall well-being, and consider a comprehensive approach to cognitive health beyond just hormone levels.
In Retrospect
the intersection of testosterone therapy and brain health presents a fascinating landscape of possibilities and inquiries. As research continues to illuminate the nuanced roles hormones play in cognitive function and emotional well-being, it becomes clear that a one-size-fits-all approach may not suffice. While testosterone therapy may offer potential benefits to some, it is essential to approach this treatment with a commitment to individual health needs and guided by professional oversight. As we navigate this intricate journey, staying informed and engaged with ongoing research will empower us to make educated decisions regarding our health. Ultimately, the quest for optimal brain health is a multifaceted endeavor—one that emphasizes the importance of understanding ourselves holistically and embracing the complexity of our biology.