In recent years, the conversation surrounding testosterone therapy has surged from whispers to a booming discussion, captivating the attention of both medical professionals and the general public alike. Among the various methods available, injectable testosterone therapy has emerged as a focal point, offering men and women alike a potent option for addressing hormonal imbalances and enhancing quality of life. But what lies beneath the surface of this injectable solution? This article delves into the intricacies of testosterone therapy—exploring its benefits, risks, and the science that underpins its use. Whether you’re contemplating treatment for low testosterone levels or simply seeking to understand this medical trend, join us as we navigate the landscape of injectable testosterone therapy, illuminating its potential and unveiling the nuances of a choice that has become both a lifeline and a topic of debate in contemporary health discussions.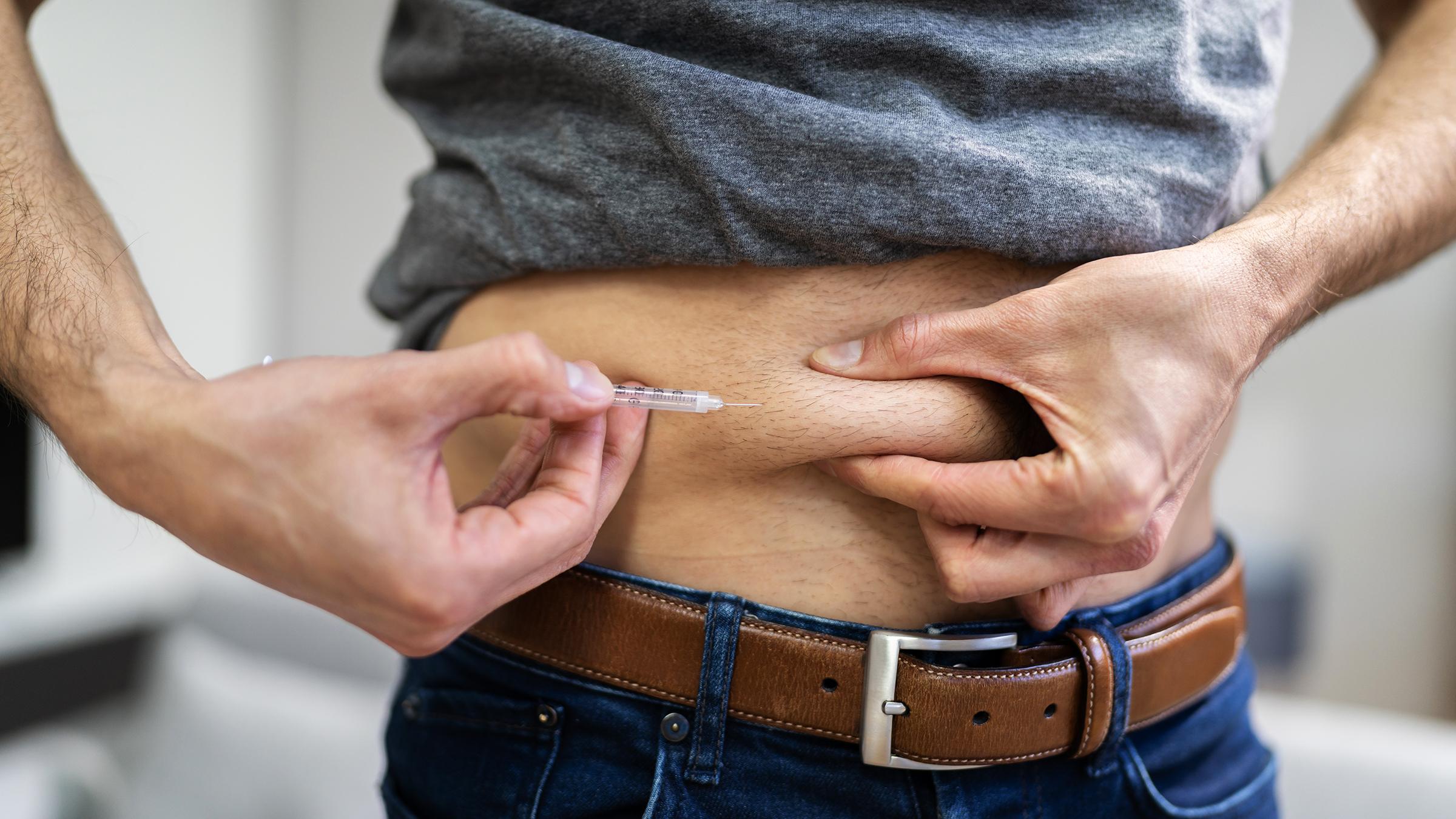
Understanding Injectable Testosterone Therapy and Its Benefits
Injectable testosterone therapy has emerged as a pivotal treatment option for individuals experiencing hormonal imbalances, particularly men suffering from low testosterone levels, commonly referred to as hypogonadism. This therapy involves administering testosterone through intramuscular or subcutaneous injections, which allows for precise dosage and quick absorption into the bloodstream. Unlike oral alternatives, injectable forms bypass liver metabolism, leading to more stable hormone levels and minimizing the risk of side effects. Some of the key advantages include:
- Improved Energy Levels: Patients often report enhanced stamina and reduced fatigue.
- Increased Muscle Mass: Regular injections promote muscle growth and strength, making them beneficial for athletes and bodybuilders.
- Enhanced Mood: Testosterone therapy can combat symptoms of depression and anxiety, leading to better overall mental health.
- Better Libido: Improved sexual function and desire are significant benefits for many undergoing therapy.
While injectable testosterone therapy offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to understand the appropriate dosage and frequency to minimize potential risks. Healthcare providers typically tailor a regimen based on individual needs, often starting with an initial dosage and adjusting as necessary. Monitoring blood levels and evaluating symptoms are crucial in this process. Here’s a simple table to illustrate common injection schedules:
| Injection Frequency | Common Dosage | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Every 1-2 weeks | 100-200 mg | Standard hormone replacement |
| Every 3-4 weeks | 200-300 mg | Longer-acting formulations |
Evaluating Eligibility: Who Can Benefit from Hormone Replacement
Determining eligibility for injectable testosterone therapy involves assessing various physical and psychological factors. Individuals who may benefit from this treatment often exhibit symptoms associated with low testosterone levels, such as fatigue, decreased libido, and mood swings. Additionally, medical history plays a crucial role; candidates typically include those with conditions like hypogonadism, as well as older adults experiencing age-related hormonal decline. A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional can assess testosterone levels through blood tests and consider symptoms along with potential benefits versus risks of the therapy.
Other factors influencing eligibility include lifestyle choices and underlying health conditions. For instance, individuals with obesity, diabetes, or specific heart conditions may require special attention before starting treatment. Factors such as age, general health, and medication interactions should not be overlooked. The following conditions or characteristics generally signify that one might be a suitable candidate for injectable testosterone therapy:
- Low testosterone levels confirmed through lab tests
- Signs of low testosterone such as low energy or mood difficulties
- Age-related decline not primarily associated with other medical issues
- No history of prostate cancer or severe sleep apnea
Navigating Treatment Options: Types and Administration Methods
When considering injectable testosterone therapy, patients typically encounter a range of options regarding the type of testosterone to be administered. The most common forms include testosterone enanthate, testosterone cypionate, and testosterone propionate. Each variant differs in its release time and duration of action, which can affect how often injections are needed and how stable testosterone levels remain in the bloodstream. For example, enanthate and cypionate are generally long-acting, requiring administration every 1 to 2 weeks, while propionate is shorter-acting and necessitates more frequent injections.
The method of administration also plays a crucial role in treatment efficacy and patient comfort. Injections can be performed via intramuscular (IM) or subcutaneous (SC) routes. IM injections typically involve larger needles and are administered into major muscle groups, such as the thigh or buttocks, allowing for faster absorption. Conversely, SC injections utilize smaller needles and can be given in specific areas like the abdomen, promoting a more gradual release into the bloodstream. Understanding these options helps individuals tailor their treatment to fit their lifestyle and preferences.
| Type of Testosterone | Administration Frequency | Administration Method |
|---|---|---|
| Testosterone Enanthate | Every 1-2 weeks | Intramuscular |
| Testosterone Cypionate | Every 1-2 weeks | Intramuscular |
| Testosterone Propionate | Every 2-3 days | Intramuscular |
| Testosterone Undecanoate | Every 10-14 weeks | Intramuscular |
| Subcutaneous Testosterone | Weekly or bi-weekly | Subcutaneous |
Monitoring Progress: Key Indicators of Success in Therapy
When undergoing injectable testosterone therapy, tracking specific indicators can provide insight into the effectiveness of the treatment. Symptom relief is one of the most significant indicators; individuals often report improvements in mood, energy levels, and libido. Other noticeable changes may include physical transformations, such as increased muscle mass and reduced body fat, which serve as tangible evidence of therapy efficacy. It’s essential to create a baseline measurement prior to starting treatment to observe these changes over time.
Regular monitoring through blood tests is crucial for assessing hormone levels. Key indicators include serum testosterone levels, estradiol levels, and hematocrit percentages. Utilizing a table to summarize these metrics can provide a clear overview of progress:
| Indicator | Baseline Level | Current Level | Target Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum Testosterone | 300 ng/dL | 600 ng/dL | 400-800 ng/dL |
| Estradiol | 30 pg/mL | 22 pg/mL | 10-40 pg/mL |
| Hematocrit | 45% | 50% | 38-52% |
Additionally, mental health assessments can provide a deeper understanding of psychological progress throughout the therapy. Keeping a log of any mood fluctuations and overall mental well-being can help both patients and healthcare providers make informed adjustments to the treatment plan as necessary.
Potential Risks and Side Effects: What Patients Should Know
While injectable testosterone therapy can offer significant benefits for those with low testosterone levels, it is important for patients to be aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with treatment. Commonly reported side effects may include acne, hair loss, and mood changes, stemming from hormonal fluctuations in the body. In some cases, patients may experience increased aggression or irritability, which can impact personal relationships and overall well-being. Here are other possible risks to consider:
- Cardiovascular Issues: Elevated red blood cell count can lead to increased risks of heart attack or stroke.
- Sleep Apnea: Testosterone therapy may exacerbate or contribute to sleep apnea.
- Infertility: Long-term use can affect sperm production, impacting fertility.
- Liver Problems: Though rare, injectable testosterone can sometimes lead to liver complications.
Moreover, it’s essential to monitor testosterone levels regularly during treatment to mitigate adverse outcomes like hormonal imbalances. Some patients might also experience localized reactions at the injection site, such as pain, swelling, or bruising. Understanding these aspects can prepare individuals for a more informed discussion with their healthcare provider. Below is a summarizing table of potential effects:
| Potential Side Effect | Notes |
|---|---|
| Acne | Can occur due to increased oil production. |
| Cardiovascular Problems | Monitor for sudden changes in health. |
| Infertility | May be reversible upon discontinuation. |
| Sleep Apnea | Consult with a specialist if symptoms arise. |
Enhancing Outcomes: Lifestyle Changes to Support Therapy
Adopting certain lifestyle changes can significantly enhance the effects of injectable testosterone therapy, leading to improved overall well-being. Regular physical activity plays a critical role in optimizing hormone levels; incorporating strength training and cardiovascular exercises into your routine can boost testosterone production and enhance muscle mass. Moreover, maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients can support hormonal health. Consider including foods high in zinc and omega-3 fatty acids, such as:
- Shellfish
- Leafy greens
- Fatty fish
- Nuts and seeds
In addition to diet and exercise, quality sleep is essential for hormone regulation. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night to promote the body’s natural recovery processes and support testosterone levels. Stress management techniques, such as meditation and mindfulness, are equally vital. Chronic stress can elevate cortisol levels, negatively impacting testosterone. Below is a simple table outlining effective stress management strategies:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Meditation | Practice mindfulness to reduce anxiety and enhance emotional regulation. |
| Yoga | Engage in movements that increase flexibility and promote relaxation. |
| Deep Breathing | Utilize breathing techniques to calm the nervous system. |
Consultation and Communication: Working Effectively with Healthcare Providers
Establishing a strong foundation of trust and communication with your healthcare provider is essential for a successful experience with injectable testosterone therapy. To foster this relationship, consider the following strategies:
- Be Prepared: Gather your medical history, current medications, and any symptoms you are experiencing.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to enquire about treatment options, dosages, and potential side effects.
- Set Goals: Discuss your objectives for the therapy, whether they are related to energy levels, mood improvement, or physical performance.
Moreover, ongoing communication is crucial in monitoring your progress and adjusting your treatment as necessary. Regular follow-ups can help identify any concerns and ensure the therapy is having the desired effect. Keep in mind the importance of understanding your provider’s recommendations and openly sharing any side effects you may experience. To aid in this process, consider maintaining a journal to track your symptoms and responses over time. This can facilitate more productive discussions during your appointments.
Q&A
Q&A on Injectable Testosterone Therapy
Q1: What is injectable testosterone therapy?
A1: Injectable testosterone therapy involves administering testosterone hormone through injections to help raise testosterone levels in individuals diagnosed with low testosterone, also known as hypogonadism. It aids in restoring hormonal balance and is often used in men who may experience symptoms due to declining hormone levels, such as fatigue, low libido, and decreased muscle mass.
Q2: How is the therapy administered?
A2: This therapy is primarily delivered via intramuscular or subcutaneous injections, depending on the specific formulation and the healthcare provider’s recommendation. Patients may receive injections in a clinical setting or self-administer at home after appropriate training.
Q3: Who is a candidate for injectable testosterone therapy?
A3: Candidates typically include men with confirmed low testosterone levels and accompanying symptoms. These can include decreased energy, mood changes, difficulty concentrating, and reduced sexual function. Women may also seek testosterone therapy for specific conditions, but this requires careful monitoring and is less common.
Q4: What are the common forms of injectable testosterone?
A4: The most common forms include testosterone cypionate, testosterone enanthate, and testosterone undecanoate. Each has slightly different release profiles and dosing schedules, influencing how often injections are required—ranging from weekly to every few weeks.
Q5: What benefits can individuals expect from this therapy?
A5: Patients often report improvements in energy levels, mood stabilization, enhanced libido, increased muscle mass, and better concentration. The therapy aims to restore vitality and overall well-being while addressing symptoms associated with low testosterone.
Q6: Are there risks or side effects associated with injectable testosterone therapy?
A6: Yes, like any medical treatment, testosterone therapy comes with potential risks and side effects. These can include acne, fluid retention, increased red blood cell count, sleep apnea, and potential changes in cholesterol levels. It is crucial for patients to engage in regular follow-up appointments to monitor for these effects.
Q7: How is success measured in testosterone therapy?
A7: Success is typically measured through a combination of objective and subjective assessments. This includes regular blood tests to monitor testosterone levels, alongside evaluations of symptom relief and quality of life improvements reported by the patient.
Q8: What lifestyle changes should accompany testosterone therapy?
A8: While testosterone therapy can offer significant benefits, adopting a healthy lifestyle is equally important. This may involve regular exercise, a balanced diet, weight management, and good sleep hygiene—all of which can help improve overall health and enhance the effectiveness of the therapy.
Q9: Is injectable testosterone therapy safe for long-term use?
A9: Long-term use can be safe for many individuals when administered under the supervision of a healthcare provider. However, regular evaluations are important to mitigate risks and ensure that treatment remains appropriate and beneficial.
Q10: What should individuals consider before starting injectable testosterone therapy?
A10: Before starting therapy, individuals should consult with a healthcare professional to discuss their medical history, current health status, and the potential benefits and risks. It is also essential to have a comprehensive understanding of how therapy might affect their lifestyle and overall health.
Concluding Remarks
injectable testosterone therapy presents a nuanced landscape in the realm of hormonal health. While it may offer promising benefits for individuals grappling with low testosterone levels, it is essential to navigate this journey with caution and awareness. From the science behind the treatment to the personal stories that resonate with many, the decision to engage in this therapy should be approached thoughtfully and in consultation with healthcare professionals. As our understanding of hormone regulation continues to evolve, so too does the narrative surrounding testosterone therapy—one that invites ongoing dialogue, research, and reflection. Ultimately, the path to wellness is as unique as each individual, and knowledge remains the most potent ally in making informed choices for better health.










