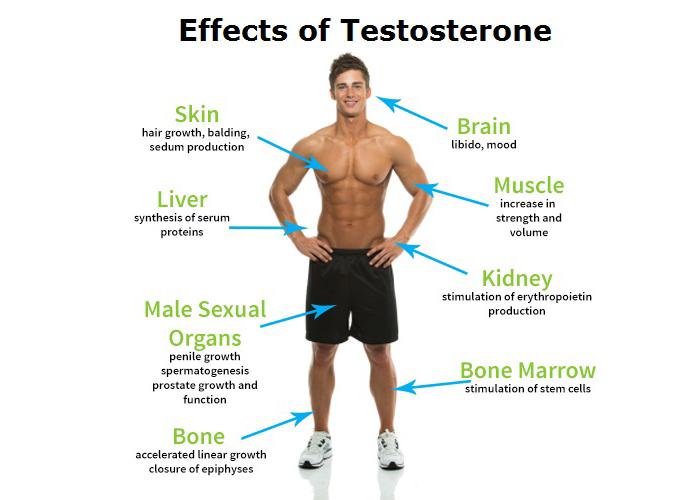
In the intricate tapestry of human biology, hormones play an essential role, subtly influencing everything from mood and energy levels to muscle mass and libido. Among these powerful substances, testosterone stands out—not only as a key player in male health but also as a vital component in the well-being of individuals of all genders. For many, the gradual decline of this critical hormone can lead to a myriad of challenges, including fatigue, diminished motivation, and changes in physical composition. As the conversation around testosterone deficiency gains momentum, so too does the interest in testosterone therapy—a treatment that aims to restore balance and rejuvenate the body. This article delves into the world of testosterone therapy, exploring its benefits, risks, and the evolving understanding of hormonal health in the quest for vitality and wellness.
Understanding Testosterone Deficiency and Its Impact on Health
Testosterone deficiency, often referred to as low T, can significantly alter a person’s physical, emotional, and sexual well-being. It’s not merely a condition of the body but one that intricately affects mental health as well. Men experiencing low testosterone levels may find themselves grappling with a range of symptoms, such as:
- Fatigue: An overwhelming sense of tiredness that can impact daily life.
- Weight Gain: Hormonal imbalances can lead to increased body fat, especially around the abdomen.
- Reduced Libido: A noticeable drop in sexual desire can occur.
- Emotional Changes: This may include mood swings, depression, or irritability.
The implications of testosterone deficiency extend beyond individual symptoms, often leading to long-term health challenges. Notably, untreated low testosterone can increase the risk of conditions such as:
| Health Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Disease | Low testosterone has been linked to increased heart disease risk. |
| Osteoporosis | Reduced bone density, leading to a higher risk of fractures. |
| Diabetes | Low T levels are associated with insulin resistance. |
Recognizing these risks is crucial as it fosters early intervention and management. Seeking testosterone therapy can be a vital step toward restoring hormonal balance and enhancing overall health outcomes.
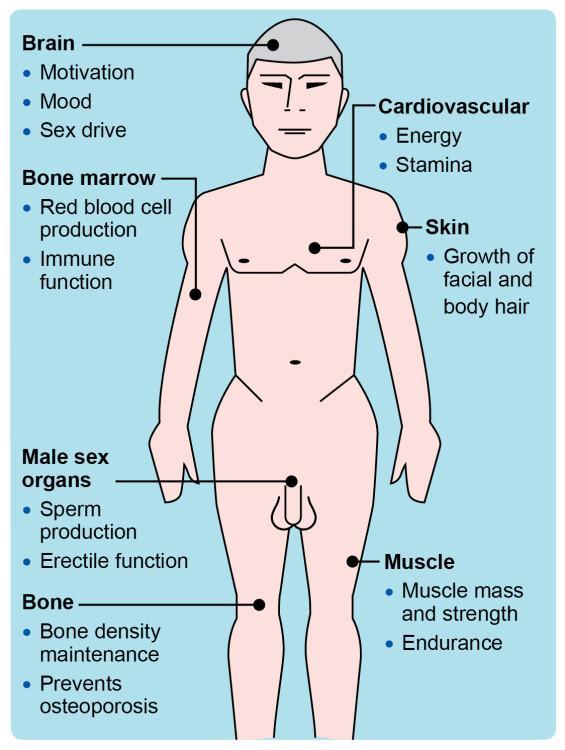
Exploring the Benefits and Risks of Testosterone Therapy
Testosterone therapy has gained popularity as a treatment for testosterone deficiency, offering a range of potential benefits that can significantly enhance the quality of life for many individuals. Common advantages include improved energy levels, enhanced mood and cognitive function, increased muscle mass and strength, and better sexual performance. Moreover, studies suggest that vitality and overall well-being can be restored, often leading to higher self-esteem and improved motivation. For some, testosterone therapy can also aid in weight management by boosting metabolism, which is especially beneficial for those struggling with obesity related to low testosterone levels.
Despite these allurements, it is crucial to approach testosterone therapy with caution, as there are noteworthy risks involved. Potential side effects may include an increased risk of cardiovascular issues, such as heart attacks and strokes, alongside negative impacts on prostate health. Other concerns may encompass hormonal imbalances that lead to mood swings, sleep apnea, or infertility. Therefore, monitoring and guidance from healthcare professionals are essential to tailor treatment to individual needs while minimizing risks. To ensure informed decisions, a thorough discussion of both benefits and risks should precede the initiation of therapy.
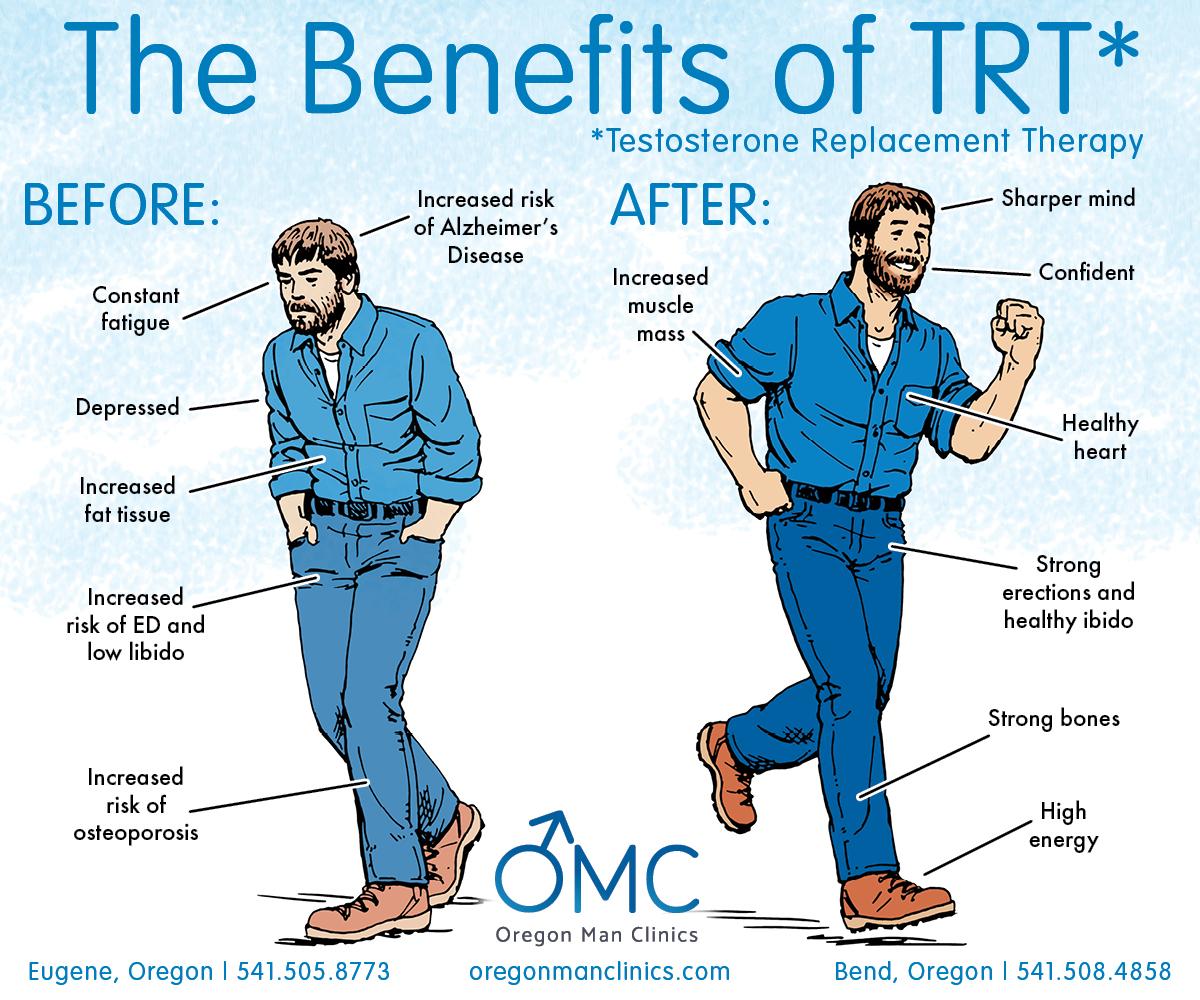
Types of Testosterone Therapy: Options and Considerations
When considering testosterone therapy, there are various options available, each catering to specific needs and lifestyles. Some of the most common methods include:
- Injections: Typically administered every one to four weeks, intramuscular injections deliver testosterone directly into the bloodstream, providing a quick boost in hormone levels.
- Patches: Transdermal patches are applied to the skin, releasing testosterone gradually. This method allows for a steady level of hormone while being easy to apply.
- Gels: Similar to patches, testosterone gels are absorbed through the skin. They offer flexibility in dosing and can be applied daily, but care must be taken to prevent unintended transfer to others.
- Pellets: Implanted under the skin, testosterone pellets release the hormone slowly over several months, providing a long-lasting option without the need for frequent applications.
Each method has its advantages and drawbacks, influencing treatment adherence and effectiveness. For example, while injections may require less frequent dosing, some patients may find the process painful or inconvenient. Conversely, patches and gels offer ease of use but may need more frequent application or adjustment to find the right dose. Factors to consider when choosing a therapy include:
- Convenience: How seamlessly can the therapy fit into daily routines?
- Cost: What are the overall expenses associated with each method?
- Side Effects: What potential side effects should be monitored and what risk is acceptable?
| Method | Frequency | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|
| Injections | Every 1-4 weeks | Moderate |
| Patches | Daily | High |
| Gels | Daily | High |
| Pellets | Every 3-6 months | High |
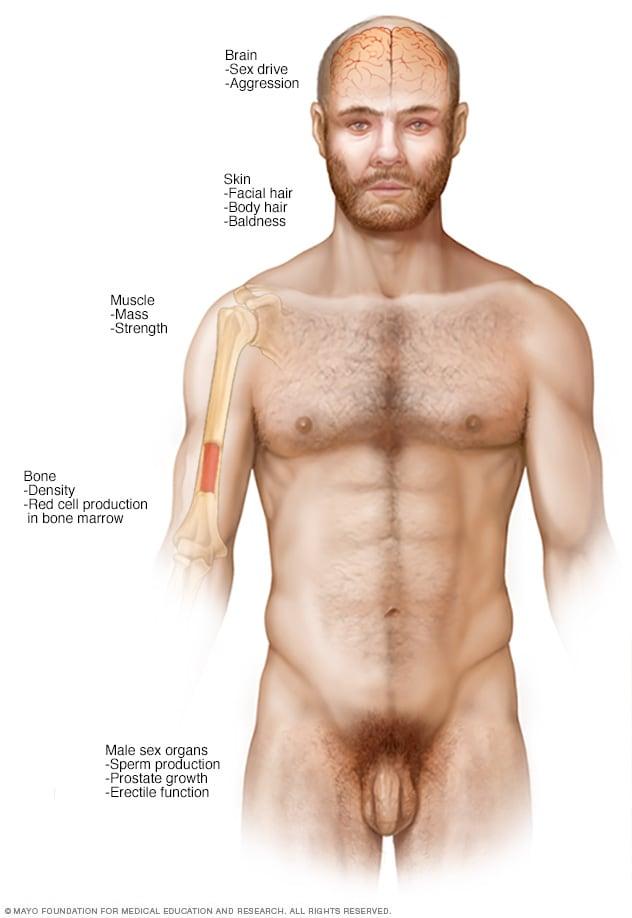
Criteria for Diagnosis: Recognizing Testosterone Deficiency Symptoms
When considering the possibility of testosterone deficiency, it’s crucial to identify a range of symptoms that may signal a disruption in hormonal balance. Common indicators of low testosterone levels can include:
- Decreased libido or sexual dysfunction
- Increased fatigue or lack of energy
- Loss of muscle mass and strength
- Weight gain, particularly around the abdomen
- Cognitive changes such as difficulty concentrating or mood swings
In clinical evaluations, healthcare professionals often utilize a multifaceted approach to diagnose testosterone deficiency. This typically involves reviewing a patient’s medical history, conducting a thorough physical examination, and performing laboratory tests. A diagnostic checklist may include:
| Assessment Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Blood Test | To measure testosterone levels |
| Symptom Questionnaire | To evaluate the severity of symptoms |
| Physical Examination | To check for physical signs of deficiency |
Navigating Treatment: Best Practices for Initiating Therapy
Embarking on testosterone therapy requires a well-thought-out approach to ensure that the treatment aligns with individual health needs and lifestyle. To begin, it is essential to have a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional who specializes in hormonal health. This evaluation should include a review of medical history, lifestyle factors, and a series of blood tests to confirm testosterone deficiency. Building a partnership with your healthcare provider is crucial, as they will guide you through the nuances of therapy, discuss potential benefits, risks, and help set realistic expectations for outcomes.
Once therapy is initiated, maintaining open lines of communication with your healthcare provider is vital. Regular follow-up appointments should be scheduled to monitor hormone levels, assess any side effects, and evaluate the overall effectiveness of the treatment plan. Consider these best practices for a smooth therapy journey:
- Educate yourself about testosterone therapy and its implications.
- Monitor your symptoms and emotional well-being regularly.
- Adhere to scheduled blood tests to track progress.
- Discuss any changes in lifestyle, such as diet and exercise, that may enhance therapy effectiveness.
When considering various treatment options, it’s important to understand the different methods available for testosterone administration. Here’s a brief overview:
| Method | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Injections | Testosterone is injected directly into the muscle. | Every 1-2 weeks |
| Transdermal Patches | Applied to the skin, releasing testosterone into the bloodstream. | Daily |
| Gels | Applied to skin, allowing absorption through the skin. | Daily |
| Pellets | Inserted under the skin, releasing testosterone gradually. | Every 3-6 months |
Choosing the right method should be a shared decision between you and your healthcare provider, taking into account factors such as lifestyle, preferences, and any pre-existing health conditions.
Monitoring and Adjusting Testosterone Levels for Optimal Results
Monitoring testosterone levels is crucial for individuals undergoing testosterone therapy. Regular blood tests can help determine if the treatment is effectively raising hormone levels to the desired range. Typically, these tests are conducted at baseline, after the initiation of therapy, and periodically thereafter. Key metrics to evaluate include:
- Total Testosterone Levels
- Free Testosterone Levels
- Estradiol Levels
- SHBG (Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin)
Adjustments to therapy may be necessary based on the results, which can guide dosage and application methods. For instance, if testosterone levels are found to be consistently below the target range, increasing the dosage may be appropriate. Conversely, levels that are too high can lead to unwanted side effects and may require a reduction. Below is a simple table that outlines potential adjustments based on testosterone levels:
| Testosterone Level | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
| Below Normal Range | Increase dosage |
| Normal Range | Maintain current dosage |
| Above Normal Range | Decrease dosage |
Lifestyle Strategies to Complement Testosterone Therapy
Incorporating healthy lifestyle habits can significantly enhance the benefits of testosterone therapy. Diet plays an instrumental role; adopting a nutrient-dense regimen rich in healthy fats, proteins, and micronutrients can help optimize hormone levels. Focus on foods like:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and broccoli are high in magnesium, which supports testosterone production.
- Lean Proteins: Chicken, fish, and legumes contribute to muscle mass and overall vitality.
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, and olive oil provide essential fatty acids crucial for hormone synthesis.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Berries and citrus fruits are packed with antioxidants that combat inflammation.
Alongside diet, incorporating regular physical activity can also make a world of difference. Engaging in resistance training and high-intensity interval workouts has been shown to positively affect testosterone levels. Additionally, managing stress through practices like mindfulness or yoga can prevent the hormonal imbalances often caused by elevated cortisol levels. A table illustrating these complementary activities can help visualize their impact:
| Activity | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Resistance Training | Boosts muscle synthesis and testosterone levels. |
| HIIT Workouts | Increases metabolic rate and hormone regulation. |
| Yoga and Meditation | Reduces stress and promotes emotional well-being. |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Testosterone Therapy for Testosterone Deficiency
Q1: What is testosterone deficiency?
A1: Testosterone deficiency, often referred to as hypogonadism, occurs when the body produces insufficient testosterone, a critical hormone for various bodily functions. This deficiency can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, reduced libido, mood changes, and diminished muscle mass.
Q2: How is testosterone deficiency diagnosed?
A2: Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. A healthcare provider will assess symptoms and may order blood tests to measure testosterone levels, usually taken in the morning when levels are at their peak.
Q3: What are the potential causes of testosterone deficiency?
A3: Causes may vary, ranging from primary testicular issues to secondary causes linked to the pituitary gland. Aging, genetic conditions, certain medications, obesity, and chronic illnesses such as diabetes or liver disease can also contribute to low testosterone levels.
Q4: How does testosterone therapy work?
A4: Testosterone therapy aims to restore testosterone levels to a normal range. It can be administered through injections, transdermal patches, gels, or pellets that release testosterone into the body gradually over time.
Q5: Who might benefit from testosterone therapy?
A5: Individuals diagnosed with low testosterone levels exhibiting symptoms can significantly benefit from therapy. This includes men who experience low libido, fatigue, and muscle loss, along with some women who might undergo hormone replacement for specific health issues.
Q6: What are the potential benefits of testosterone therapy?
A6: Those undergoing testosterone therapy may experience an improvement in energy levels, mood, libido, and overall quality of life. Some men also report increases in muscle mass, strength, and bone density.
Q7: Are there risks associated with testosterone therapy?
A7: Yes, there are potential risks. Some individuals may experience side effects such as acne, sleep apnea, or fluctuations in mood. There’s also a concern regarding prostate health, cardiovascular events, and the effect on fertility, so regular monitoring is essential.
Q8: How should one approach testosterone therapy?
A8: It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for a comprehensive assessment and personalized treatment plan. Monitoring testosterone levels and adjusting therapy as needed can help maximize benefits while minimizing risks.
Q9: Are there alternative treatments for managing testosterone deficiency?
A9: Yes, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, weight management, and stress reduction can positively impact testosterone levels. Certain supplements may also help, but it’s important to discuss these options with a healthcare provider before trying them.
Q10: Is testosterone therapy a lifelong commitment?
A10: For many, testosterone therapy may be a long-term commitment, as discontinuing treatment can lead to a return of deficiency symptoms. Regular check-ups can help determine the ongoing necessity of therapy and make adjustments based on individual health needs.
Conclusion: Exploring testosterone therapy for deficiency requires understanding its benefits and risks. Engaging in open discussions with healthcare providers can pave the way for informed decisions tailored to individual health needs.
The Conclusion
navigating the landscape of testosterone therapy for testosterone deficiency requires a careful balance of information, understanding, and individualized care. As we’ve explored, the journey from diagnosis to treatment is not merely a medical procedure, but a pathway to enhancing quality of life and well-being. While testosterone therapy offers promising benefits for many, it’s crucial to weigh these against potential risks and to engage in open dialogue with healthcare providers. Ultimately, informed choices and ongoing evaluations will help ensure that this therapeutic approach aligns with personal health goals and aspirations. As we continue to learn more about hormonal health, may we foster a deeper understanding of the complexities involved, paving the way for more tailored and effective treatments in the future.