In the intricate tapestry of human biology, hormones serve as vital threads that weave together the fabric of health and vitality. Among these, testosterone stands out, often dubbed the “male hormone,” though it plays crucial roles in all genders. As the years pass, many individuals may find their natural testosterone levels dwindling, leading to a spectrum of physical and emotional challenges. Enter testosterone therapy—a medical intervention designed to restore hormonal balance and rejuvenate well-being. But how exactly does this therapy function? In this article, we will unravel the science behind testosterone therapy, explore its mechanisms, benefits, and potential risks, and shed light on how it can be a beacon of hope for those seeking to reclaim their vitality. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of hormones and discover the multifaceted approach to addressing low testosterone levels.
Understanding Testosterone: The Hormone Behind Vitality
Testosterone therapy has been a transformative approach for many individuals seeking to restore balance in their hormonal levels, particularly as they age. This treatment involves supplementing the body’s testosterone through various methods such as injections, patches, gels, or pellets. Each method has its unique benefits and drawbacks, leading to varied experiences among users. It’s important to note that the goal of this therapy is not only to enhance energy and sex drive but also to improve overall well-being, muscle mass, and mental clarity. The therapy often requires consistent monitoring and adjustment by healthcare professionals to tailor the treatment to the individual’s evolving needs.
Understanding how testosterone therapy impacts the body can illuminate its significance in promoting vitality. During treatment, the body reacts by increasing levels of red blood cells, enhancing muscle strength, and potentially improving mood and cognitive function. Here’s a brief overview of common therapy methods and their benefits:
| Therapy Method | Administration | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Injections | Intramuscular or Subcutaneous | Quick absorption, customized dosing |
| Patches | Applied to skin | Consistent release, easy to use |
| Gels | Applied to skin | Convenient and non-invasive |
| Pellets | Inserted under the skin | Long-lasting release, minimal intervention |
By stimulating testosterone levels, this therapy can lead to numerous improvements in quality of life, allowing individuals to reclaim their vitality. It’s essential for those considering testosterone therapy to engage in thorough discussions with healthcare providers to explore personal health goals, underlying conditions, and the best treatment approach for sustained health and wellness.
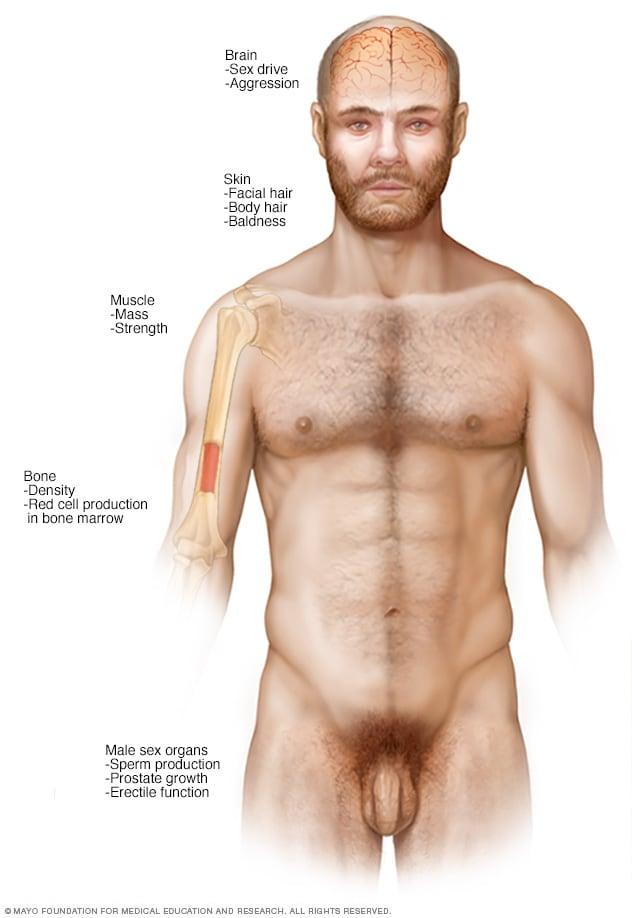
The Endocrine System: How Testosterone Production Is Regulated
The regulation of testosterone production is a complex interplay of hormones regulated by the endocrine system. In men, the hypothalamus plays a crucial role by releasing gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which in turn stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete two important hormones: luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). LH specifically targets the Leydig cells in the testes to promote testosterone synthesis, while FSH is vital for spermatogenesis. This finely tuned feedback loop maintains testosterone levels within a specific range, ensuring optimal physiological functions.
Several factors can influence this hormonal axis, including age, health, and lifestyle choices. For instance, excessive stress can elevate cortisol levels, negatively impacting testosterone production. Additionally, conditions such as obesity or diabetes can impair hormone signaling. The interaction between these elements underscores the importance of a holistic approach to hormone health. Below is a summary of some key regulators and their effects on testosterone production:
| Regulator | Impact on Testosterone |
|---|---|
| GnRH | Stimulates LH and FSH secretion |
| LH | Directly stimulates testosterone production |
| FSH | Supports sperm production |
| Cortisol | Inhibits testosterone production |
| Obesity | Reduces hormone sensitivity |
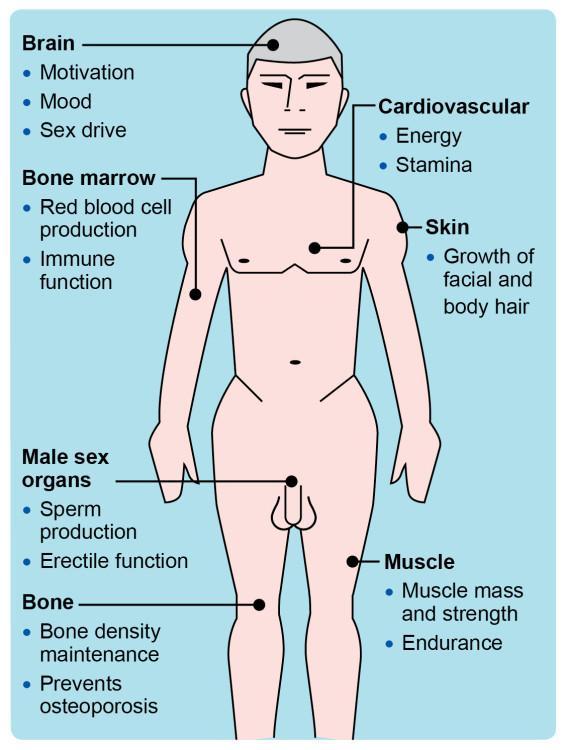
Indications for Therapy: Who Can Benefit from Testosterone Replacement
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can be advantageous for several groups of individuals experiencing low testosterone levels, commonly referred to as hypogonadism. Men typically considered for therapy may exhibit symptoms such as decreased libido, fatigue, erectile dysfunction, or reduced muscle mass. In these cases, blood tests revealing low testosterone concentration can support the decision to initiate treatment. Women, too, may benefit from TRT, particularly those in menopause or facing certain hormonal disorders, as testosterone plays a key role in maintaining overall energy levels, sexual health, and bone density.
Beyond mere symptoms, there are specific indications for initiating testosterone therapy that healthcare professionals consider. These include:
- Confirmed low testosterone levels in conjunction with clinical symptoms
- Age-related hormonal decline, typically in middle-aged and older men
- Chronic illnesses such as obesity or diabetes, which may exacerbate hormonal imbalances
- Certain genetic conditions affecting hormone production
The potential for TRT to enhance quality of life makes it a valuable option, provided that patients are properly assessed and monitored throughout their treatment journey.
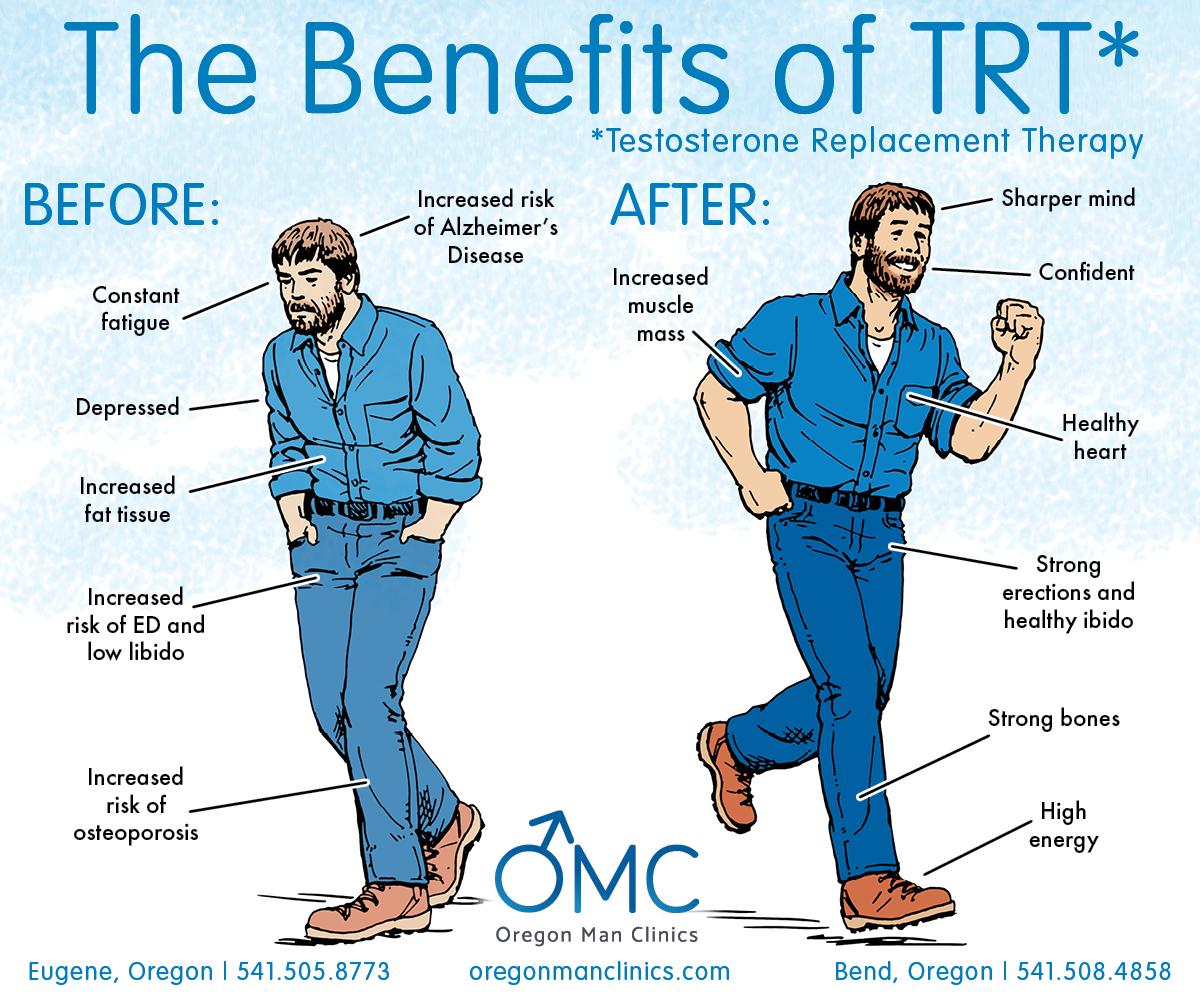
Forms of Testosterone Therapy: Navigating Treatment Options
Testosterone therapy offers a variety of forms to cater to individual preferences and medical needs. The most common methods include:
- Injectable Testosterone: Administered directly into the muscle, this method provides a quick and effective increase in testosterone levels. Doses can be given weekly or bi-weekly.
- Transdermal Patches: These patches are applied to the skin and release testosterone gradually. They are convenient and help maintain stable hormone levels throughout the day.
- Topical Gels: Similar to patches, gels are applied to the skin and absorbed into the bloodstream. They allow for flexible dosing and can be easily adjusted based on individual requirements.
- Pellets: Small pellets containing testosterone are implanted under the skin, usually in the hip area. They release testosterone gradually over several months, minimizing the need for frequent administration.
- Oral Testosterone: Although less common due to potential liver effects, certain formulations of oral testosterone are available. This method may be preferred by those who wish to avoid injections or topical applications.
| Form of Therapy | Administration Method | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Injectable | Intramuscular injection | Weekly or bi-weekly |
| Transdermal Patch | Applied to the skin | Daily |
| Topical Gel | Applied to skin surfaces | Daily |
| Pellets | Implanted under the skin | Every 3-6 months |
| Oral | Swallowed in tablet form | Daily |
Choosing the right form of testosterone therapy often depends on factors such as lifestyle preferences, medical history, and desired outcomes. Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential to tailor the treatment plan that best suits individual needs. Monitoring is vital, as testosterone levels can fluctuate, and adjustments may be necessary to ensure efficacy and minimize side effects.
The Mechanism of Action: How Testosterone Affects the Body
Testosterone exerts a pivotal influence on numerous physiological processes in the body. As a steroid hormone primarily produced in the testes for men and the ovaries and adrenal glands for women, it plays a crucial role in sexual development, muscle strength, and bone density. Once introduced into the bloodstream through therapy, testosterone binds to androgen receptors on target cells, initiating a cascade of biological effects. These effects include:
- Muscle Growth: Testosterone promotes protein synthesis, leading to increased muscle mass and strength.
- Bone Strength: It enhances bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
- Mood Regulation: The hormone contributes to improved mood, energy, and motivation levels.
- Libido Enhancement: Testosterone significantly influences sexual desire and function.
Furthermore, testosterone’s role extends to metabolic processes, influencing fat distribution and insulin sensitivity. As a result, individuals undergoing testosterone therapy may experience significant changes in body composition, such as reduced fat mass and improved metabolic health. The influence of testosterone on the body can be summarized in the table below:
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Muscle Mass | Enhances physical strength and performance. |
| Bone Density Improvement | Helps maintain stronger bones over time. |
| Fat Distribution | Aids in reducing visceral fat and reshaping body composition. |
| Enhanced Libido | Boosts sexual appetite and function. |
Monitoring Progress: Key Metrics to Assess Therapy Effectiveness
Monitoring the success of testosterone therapy involves tracking various key metrics that can indicate hormonal balance and overall health improvements. One of the primary metrics is testosterone levels themselves, which can be measured through blood tests. Regular testing can help gauge if the treatment is yielding desired results, ensuring testosterone levels fall within an optimal range. Alongside these levels, healthcare providers may also monitor symptoms reported by the patient, focusing on changes in energy, mood, libido, and physical strength, all of which can significantly impact quality of life.
Another crucial aspect to consider is metabolic health, with specific attention to factors such as body composition and cardiovascular markers. Patients may experience shifts in muscle mass and fat distribution, making body composition assessments valuable. Additionally, tracking cholesterol levels and blood pressure can help understand the broader implications of testosterone therapy on cardiovascular health. For a more comprehensive view, potential side effects like sleep apnea and hormonal imbalances should also be monitored. Employers and healthcare providers can utilize a simple table to summarize these metrics:
| Key Metrics | Measurement Frequency | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Testosterone Levels | Every 3-6 months | Ensures optimal dosing |
| Body Composition | Every 6 months | Tracks muscle gain and fat loss |
| Cholesterol Levels | Yearly | Assesses cardiovascular risk |
| Blood Pressure | Every visit | Monitors heart health |
Potential Risks and Side Effects: A Balanced Perspective on Treatment
While testosterone therapy offers numerous benefits such as improved mood, increased energy levels, and enhanced muscle mass, it is crucial to approach this treatment with a comprehensive understanding of its potential risks. Some individuals may experience side effects that range from mild to more serious, including:
- Acne and oily skin
- Sleep apnea
- Increased risk of cardiovascular issues
- Mood swings and aggression
- Excessive hair growth or hair loss
Monitoring and discussing these risks with a healthcare professional can help mitigate potential complications. It’s also important to evaluate personal health history before starting treatment, as certain conditions may predispose individuals to adverse reactions. The following table summarizes some common risks associated with testosterone therapy:
| Risk | Severity | Monitoring Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Effects | Moderate to High | Regular heart health check-ups |
| Hormonal Imbalance | Moderate | Routine hormone level tests |
| Prostate Issues | Moderate | Annual prostate screenings |
Q&A
Q&A: How Testosterone Therapy Works
Q1: What is testosterone therapy, and why do people seek it?
A1: Testosterone therapy involves the administration of testosterone to treat low testosterone levels, a condition known as hypogonadism. Many individuals seek this therapy to alleviate symptoms such as fatigue, depression, reduced libido, and decreased muscle mass. By restoring hormone levels, the therapy aims to enhance overall well-being and improve quality of life.
Q2: How is testosterone therapy administered?
A2: Testosterone therapy can be delivered through various methods, including injections, skin patches, topical gels, and pellets implanted under the skin. Each method has its pros and cons. Injections offer a more direct approach, while topical applications allow for daily administration without needles. It’s essential for individuals to discuss options with their healthcare provider to find the method that suits their lifestyle and needs.
Q3: How does testosterone work in the body?
A3: Testosterone influences numerous physiological processes. It helps regulate libido, muscle and bone strength, fat distribution, and mood. When therapy is initiated, testosterone enters the bloodstream and binds to androgen receptors in target tissues, activating a cascade of biological effects. These changes can lead to improved muscle mass, increased energy levels, and an enhanced sense of well-being, creating a ripple effect on numerous bodily functions.
Q4: Who can benefit from testosterone therapy?
A4: While primarily indicated for men with clinically low testosterone levels, women may also benefit in specific situations—for example, during menopause. However, testosterone therapy isn’t universally suited for everyone. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the appropriateness of the treatment based on individual hormone levels, symptoms, and overall health.
Q5: Are there risks associated with testosterone therapy?
A5: Yes, like any medical intervention, testosterone therapy comes with potential risks. Side effects may include sleep apnea, acne, increased red blood cell count, and heightened risk of cardiovascular events. It’s important for individuals to engage in regular follow-ups with their doctor to monitor any adverse effects and assess the therapy’s effectiveness.
Q6: How long does it take to see results from testosterone therapy?
A6: Patience is key! Individuals may begin to notice improvements in energy levels and libido within a few weeks, while physical changes, such as increased muscle mass and strength, may take several months to become evident. The timeline can vary widely among individuals, depending on their circumstances and adherence to therapy.
Q7: Can lifestyle changes enhance the benefits of testosterone therapy?
A7: Absolutely! Complementing testosterone therapy with healthy lifestyle choices can amplify its effects. Regular exercise—especially strength training—balanced nutrition, and quality sleep can all contribute to improved outcomes. Additionally, reducing stress through mindfulness or other techniques can further support hormonal balance and overall health.
Q8: Is it safe to discontinue testosterone therapy?
A8: Discontinuing testosterone therapy should always be a decision made in consultation with a healthcare provider. Abrupt cessation may lead to a return of symptoms associated with low testosterone. A gradual taper or alternative strategies may be recommended to manage hormone levels effectively.
Q9: What should individuals consider before starting testosterone therapy?
A9: Individuals should be well-informed and prepared for an ongoing partnership with their healthcare provider. This includes comprehensive evaluations, regular monitoring of testosterone levels, understanding potential side effects, and committing to lifestyle changes that support hormonal health. It’s vital to approach testosterone therapy as a long-term management strategy rather than a quick fix.
Q10: Where can one find reliable information about testosterone therapy?
A10: Reliable information can be sourced from healthcare professionals specializing in endocrinology or urology. Additionally, reputable organizations such as the American Urological Association and the Endocrine Society provide educational resources. However, personal consultation is invaluable for addressing unique questions and concerns regarding testosterone therapy.
This Q&A aims to provide a balanced insight into testosterone therapy, serving as a resource for those considering treatment or seeking to understand the nuances of hormonal health.
In Summary
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of testosterone therapy, it’s clear that this complex intervention carries both promise and responsibility. Understanding how testosterone functions within the body opens the door to potential benefits for those who may need a boost in their hormonal balance. Yet, like all medical treatments, it invites careful consideration of the risks and rewards.
Whether you are contemplating testosterone therapy for yourself or simply seeking to educate yourself about the intricacies of hormone health, it is vital to remain informed and to engage in open dialogues with healthcare professionals. Knowledge empowers us to make choices that align with our personal health goals and overall well-being.
In the world of medicine, every treatment is a step on a journey toward understanding and betterment. With testosterone therapy, that journey can illuminate paths to improved vitality and quality of life. As you venture forth, may you find clarity in the complexities of hormone therapy and confidence in the decisions that will shape your health landscape.










