In a world increasingly preoccupied with the delicate balance of metabolic health, the conversation surrounding testosterone therapy has emerged as a focal point of interest and inquiry. Once relegated to the confines of athletic enhancement and age-related decline, testosterone is now recognized for its multifaceted role in various bodily functions, including metabolism, mood regulation, and overall well-being. As research unveils the intricate connections between hormone levels and metabolic pathways, many are left wondering: can testosterone therapy hold the key to unlocking improved health outcomes for those grappling with metabolic disorders? In this article, we delve into the science and implications of testosterone therapy, exploring its potential benefits, associated risks, and the ongoing debates that shape this evolving field of medicine. Whether viewed through the lens of traditional endocrinology or the emerging perspectives of integrative health, the discussion promises to illuminate new possibilities for achieving metabolic balance in an ever-changing landscape of health care.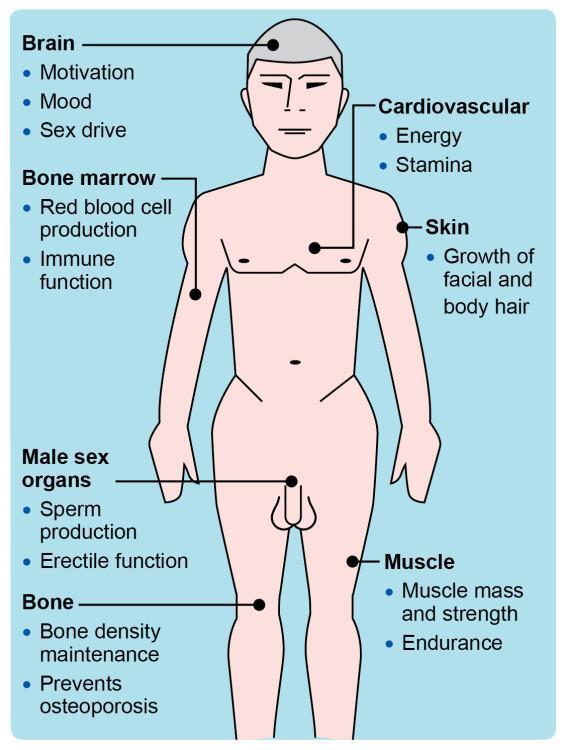
Understanding Testosterones Role in Metabolic Health
Testosterone, primarily recognized as a male hormone, plays a vital role not only in muscle development and libido but also in metabolic health. An optimal level of testosterone is crucial for maintaining body composition and functionality. When testosterone levels are low, this can lead to adverse metabolic effects such as increased fat mass, reduced muscle mass, and insulin resistance. Addressing testosterone deficiencies through therapy may help mitigate these effects, ensuring a more balanced metabolism and potentially lowering the risk of conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Research indicates that men with higher testosterone levels often show improved metabolic parameters, including better glucose metabolism and lipid profiles. Some of the key benefits of testosterone in metabolic health include:
- Improved insulin sensitivity: Enhances the body’s response to insulin, regulating blood sugar levels effectively.
- Increased lean muscle mass: Muscle tissue burns more calories at rest, influencing overall energy expenditure.
- Reduction in body fat: Helps in mobilizing fat stores, thus promoting weight loss or maintenance.
- Enhanced energy levels: Contributes to improved physical activity, encouraging a healthier lifestyle.
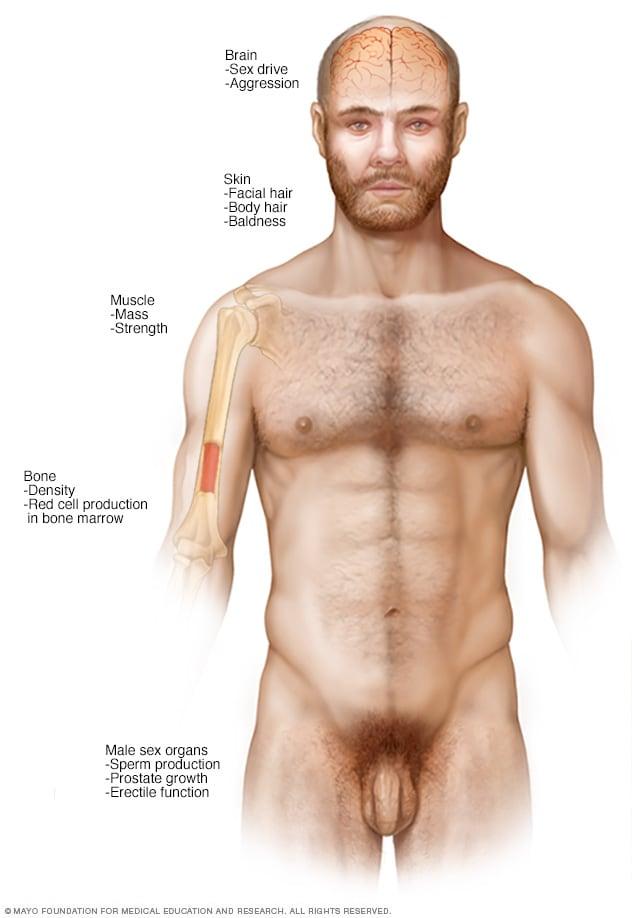
Exploring the Benefits of Testosterone Therapy for Insulin Sensitivity
Testosterone therapy has emerged as a focal point in the discussion of metabolic health, particularly concerning insulin sensitivity. Insulin resistance can lead to numerous health complications, including type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. By enhancing testosterone levels, studies suggest a noteworthy improvement in metabolic parameters. Patients undergoing testosterone therapy may experience improved glucose metabolism, which subsequently enhances the body’s ability to utilize insulin efficiently. This leads to a reduced risk of developing insulin-related diseases and can even play a role in weight management, as improved insulin sensitivity aids in maintaining a healthy weight.
Furthermore, the interplay between testosterone and fat distribution cannot be overlooked. With adequate testosterone levels, patients may witness a shift in body composition, favoring lean muscle mass over fat accumulation. This shift can result in additional benefits such as:
- Increased Energy Levels: Enhanced testosterone levels can contribute to overall vitality.
- Improved Mood: Testosterone therapy has been linked to better emotional well-being.
- Cardiovascular Health Benefits: Better insulin sensitivity also correlates with improved heart health.
As researchers delve deeper, it becomes increasingly clear that testosterone therapy may serve as a multi-faceted approach to not only boost energy and mood but also to refine metabolic functionality through enhanced insulin sensitivity.
Evaluating the Risks: Weighing the Pros and Cons of Treatment
When contemplating testosterone therapy for metabolic health, it’s critical to evaluate both the advantages and disadvantages. Among the benefits, improved insulin sensitivity, enhanced energy levels, and potential weight loss are paramount. Men experiencing low testosterone often report revitalization in mood and physical performance, which can translate into a more active lifestyle. Additionally, a healthier balance of hormones can lead to better metabolic outcomes, potentially reducing the risk of conditions like type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Conversely, the therapy also carries certain risks that cannot be overlooked. Potential side effects include acne, sleep apnea, and an increased risk of cardiovascular issues. There’s also the question of dependency, as some individuals may find themselves relying on therapy to maintain their energy levels. Below are some risks to consider:
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Issues | Increased risk of heart attack or stroke |
| Hormonal Imbalance | Potential fluctuation in mood and libido |
| Skin Reactions | Possible acne or irritation |
| Dependency | Reliance on therapy for normal functioning |
Personalizing Testosterone Therapy: Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Personalizing testosterone therapy requires careful consideration of individual patient profiles, including age, medical history, and specific metabolic needs. The goal is to tailor the dosage and administration to optimize health benefits while minimizing risks. Typically, testosterone can be administered through various methods, including:
- Injections: Often given every 1 to 3 weeks, they provide a rapid increase in testosterone levels.
- Patches: These are applied to the skin, releasing testosterone over a 24-hour period, providing a steady dosage.
- Gels or Creams: Topical applications allow for dose adjustments and are absorbed directly through the skin.
- Pellets: Implanted under the skin, these provide long-lasting testosterone delivery for up to 6 months.
Determining the appropriate dosage is equally crucial. A starting dose is often based on baseline testosterone levels and symptoms. Clinicians should follow up at regular intervals to monitor both testosterone levels and correspondingly track metabolic health markers. Adjustments may be necessary based on patient response, such as:
| Parameter | Initial Range | Adjustment Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Testosterone Level | 300-1000 ng/dL | Increase if below threshold |
| Symptom Relief | Subjective evaluation | Adjust dosage for optimal feeling |
| Side Effects | Monitor for adverse symptoms | Decrease dosage if problematic |
Lifestyle Modifications to Enhance the Effects of Testosterone Therapy
Integrating certain lifestyle modifications can significantly amplify the results of testosterone therapy, propelling you towards enhanced metabolic health. Regular physical activity is crucial; engaging in both aerobic exercises and strength training can increase testosterone levels naturally while complementing the effects of therapy. Additionally, mindful eating habits that focus on nutrient-dense foods—rich in healthy fats, protein, and antioxidants—support hormonal balance. Aim for a diet that includes:
- Lean meats and fish
- Nuts and seeds
- Leafy greens and colorful vegetables
- Whole grains
Equally important is ensuring adequate sleep and stress management. Poor sleep can negatively influence testosterone levels, so maintaining a consistent sleep routine is key. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation or yoga, can reduce stress, which otherwise may lead to hormonal imbalance. Setting a schedule that prioritizes self-care, alongside therapies like massage or relaxation techniques, can further enhance results. Consider the following table for a quick reference on effective lifestyle changes:
| Change | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Regular exercise | Boosts testosterone and overall health |
| Healthy diet | Supports hormone balance and weight management |
| Quality sleep | Improves recovery and hormonal regulation |
| Stress reduction | Enhances mental health and hormonal stability |
Monitoring and Assessing Progress: Key Indicators of Success
Effectively monitoring the effects of testosterone therapy on metabolic health hinges on a set of defined indicators that reflect both physiological and psychological changes. Hormonal levels should be evaluated regularly, including total and free testosterone, as well as estrogen and SHBG (sex hormone-binding globulin) levels. Changes in body composition, such as a reduction in visceral fat and an increase in lean muscle mass, also serve as critical indicators. Additionally, the improvement in metabolic markers like blood glucose levels, lipid profiles, and blood pressure can indicate the therapy’s success in enhancing metabolic health.
Patient-reported outcomes play an equally important role in assessment. Regular feedback on energy levels, mood, and overall quality of life should be collected through validated questionnaires. Furthermore, tracking exercise performance and physical endurance can provide a tangible measure of the therapy’s impact. The following table outlines essential indicators for monitoring progress during testosterone therapy:
| Indicator | Method of Assessment | Frequency of Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Hormonal Levels | Blood Tests | Every 3-6 months |
| Body Composition | DEXA Scan / Skinfold Measurements | Every 6 months |
| Metabolic Markers | Blood Tests | Every 3-6 months |
| Quality of Life | Patient Questionnaires | Every visit |
Future Directions: The Evolving Landscape of Hormonal Treatments for Metabolism
The landscape of hormonal treatments for metabolic health is undergoing significant transformation, driven by advancements in research and technology. As our understanding of testosterone’s role in metabolism deepens, new therapeutic approaches are emerging that aim to optimize metabolic function while reducing risks associated with traditional therapies. These developments are particularly crucial as evidence mounts regarding the link between low testosterone levels and various metabolic disorders, including obesity, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia.
Future directions in testosterone therapy may involve personalized treatment protocols that consider individual hormonal profiles, lifestyle factors, and genetic predispositions. Key areas of exploration include:
- Combination therapies: Integrating testosterone with other metabolic enhancers, such as peptides or lifestyle interventions, to maximize health outcomes.
- Delivery methods: Investigating novel delivery systems, such as subcutaneous implants or transdermal applications, for improved bioavailability and patient compliance.
- Long-term safety profiles: Continuous monitoring and research to assess the long-term effects of testosterone therapy on metabolic health.
As researchers strive to establish clear guidelines for effective treatment modalities, an emphasis on *data-driven approaches* is becoming increasingly essential. A comprehensive overview of potential side effects and benefits from ongoing studies can be structured in the following table:
| Potential Benefits | Possible Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Improved insulin sensitivity | Hormonal imbalance |
| Enhanced muscle mass | Sleep apnea |
| Better mood and cognitive function | Cardiovascular risks |
| Increased energy levels | Skin reactions |
Q&A
Q&A: Testosterone Therapy for Metabolic Health
Q1: What exactly is testosterone therapy and how does it relate to metabolic health?
A1: Testosterone therapy involves administering testosterone to individuals with low levels of this hormone, often seen in men due to aging or certain health conditions. It plays a crucial role in various metabolic processes, including fat distribution, muscle mass maintenance, and metabolic rate. By optimizing testosterone levels, individuals may experience improvements in body composition and overall metabolic function.
Q2: Who may benefit from testosterone therapy for metabolic health?
A2: Testosterone therapy could be beneficial for men with clinically low testosterone levels, particularly those experiencing symptoms like fatigue, depression, decreased libido, and changes in body composition. It is also being explored in certain populations of women, especially post-menopausal women, who may benefit from hormonal balance in relation to metabolic processes.
Q3: What evidence supports the use of testosterone therapy for metabolic health?
A3: Research suggests that testosterone therapy can lead to improved insulin sensitivity, reduced fat mass, and increased lean muscle mass, all of which contribute positively to metabolic health. Some studies have shown lower blood sugar levels and better lipid profiles in men undergoing therapy, but further research is needed to fully establish these benefits.
Q4: Are there any risks associated with testosterone therapy?
A4: Yes, while testosterone therapy can offer benefits, it is not without risks. Potential side effects include increased red blood cell count, sleep apnea, acne, breast enlargement, and an increased risk of prostate issues. It’s essential for individuals to discuss these risks with their healthcare provider before starting therapy.
Q5: How does one determine if they are a candidate for testosterone therapy?
A5: Candidates typically undergo a thorough evaluation, including a review of symptoms and blood tests to measure testosterone levels. A healthcare provider will consider age, overall health, lifestyle factors, and the presence of symptoms indicative of low testosterone before recommending therapy.
Q6: Is testosterone therapy a standalone solution for metabolic health issues?
A6: No, testosterone therapy should not be viewed as a magic bullet. It is most effective when combined with lifestyle changes like a balanced diet, regular exercise, and weight management. These complementary strategies are crucial for enhancing metabolic health and achieving sustainable results.
Q7: What does the future hold for testosterone therapy and its role in metabolic health?
A7: As research continues, we may see more tailored approaches to testosterone therapy, focusing on individualized treatment plans that consider genetic, hormonal, and lifestyle factors. Additionally, increasing awareness about metabolic health may prompt further exploration into how testosterone levels interact with metabolic diseases, leading to refined treatment protocols and better outcomes for patients.
Q8: Where can readers find more reliable information about testosterone therapy?
A8: Readers seeking more information can consult reputable medical websites, and peer-reviewed journals focusing on endocrinology and metabolic health. It’s always advisable to discuss findings with a healthcare professional to ensure they are relevant and applicable to individual circumstances.
Feel free to adapt any part of this Q&A to better suit your article’s direction or intended audience!
The Conclusion
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of testosterone therapy and its intricate relationship with metabolic health, it becomes clear that this multifaceted subject is as nuanced as the hormonal dance that governs our bodies. While the potential benefits of testosterone therapy can ignite hope for many grappling with metabolic issues, it is essential to approach this treatment with a balanced perspective.
The pathway to optimal metabolic health is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it requires a careful consideration of individual circumstances, medical histories, and the guidance of healthcare professionals. As research continues to unfold, we find ourselves at the cusp of greater understanding—one that encourages us to think critically and embrace personalized approaches to wellness.
Ultimately, the journey towards metabolic health involves more than just hormones; it encompasses lifestyle choices, nutrition, and self-awareness. As we navigate this landscape, let us remain open to the possibilities, informed by evidence, and guided by the wisdom of both science and experience. The quest for balance and well-being is ongoing, and testosterone therapy may indeed play a pivotal role for some, inviting us all to rethink the contours of health in a new light.










