Unlocking Wellness: The Role of Testosterone Therapy in Managing Metabolic Syndrome
In the intricate tapestry of human health, hormones play an essential role, influencing everything from mood to metabolism. Among these, testosterone often emerges as a focal point, revered for its quintessential contributions to overall vitality. Yet, for many, this potent hormone’s potential remains shrouded in misconceptions and stigma. Enter metabolic syndrome—an insidious cluster of conditions that elevates the risk for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. As the prevalence of this syndrome rises worldwide, new avenues for intervention are being explored, prompting a closer examination of testosterone therapy. This article delves into the intersection of testosterone and metabolic syndrome, highlighting emerging research, potential benefits, and the nuanced considerations surrounding this therapeutic approach. Join us as we navigate this complex landscape, shedding light on how hormone levels may offer a key to unlocking better health for those grappling with metabolic challenges.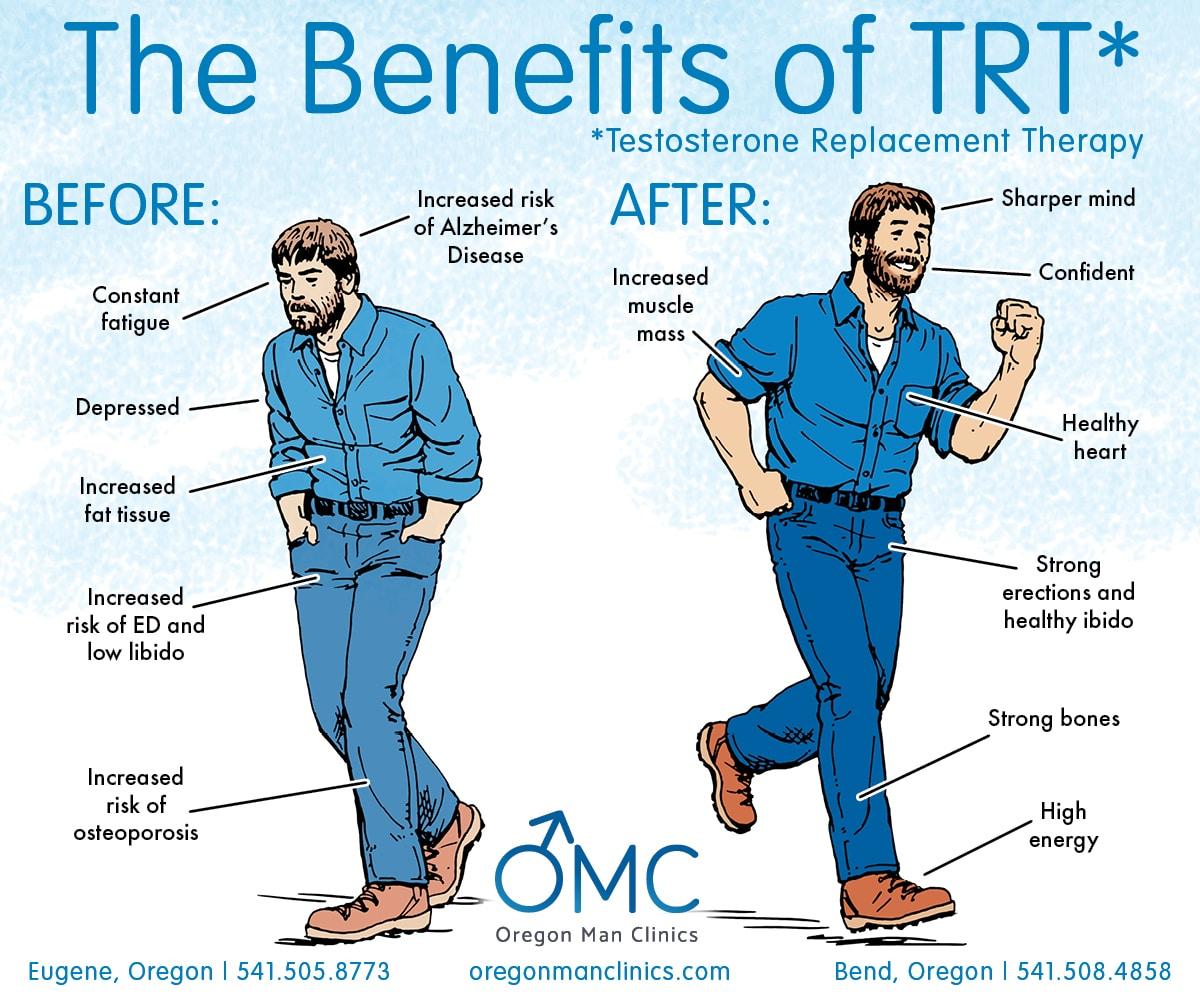
Understanding Metabolic Syndrome and Its Implications for Health
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that increase an individual’s risk for heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. These conditions include increased blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels. The implications of metabolic syndrome are profound, as they can lead to serious health complications if left unmanaged. Individuals with this syndrome often face an uphill battle with their overall well-being, facing a complicated relationship between lifestyle choices, hormonal balance, and metabolic health.
One potential intervention for managing metabolic syndrome is testosterone therapy, which has garnered attention for its role in hormonal regulation and metabolic improvement. Research suggests that testosterone can influence various biological pathways, including those associated with fat distribution and muscle mass maintenance. Consider the following benefits of testosterone therapy:
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Reduction in visceral fat
- Increased muscle mass and strength
- Enhanced lipid profile
It’s important to note that while testosterone therapy may offer several advantages, it is not a panacea. Proper assessment and monitoring are vital to tailor treatment plans that take into account personal health conditions and lifestyle factors.
The Role of Testosterone in Metabolic Function and Hormonal Balance
Testosterone plays a pivotal role in enhancing metabolic function, influencing everything from fat distribution to muscle mass. Low levels of this crucial hormone can lead to various metabolic derangements, including insulin resistance and increased visceral fat. The interconnection between testosterone and metabolism is significant, as adequate testosterone levels can promote efficient energy utilization and support glycemic control. Research indicates that testosterone therapy may help mitigate symptoms of metabolic syndrome, providing benefits such as:
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Enhanced muscle development and strength
- Reduction in body fat percentage
- Better lipid profiles
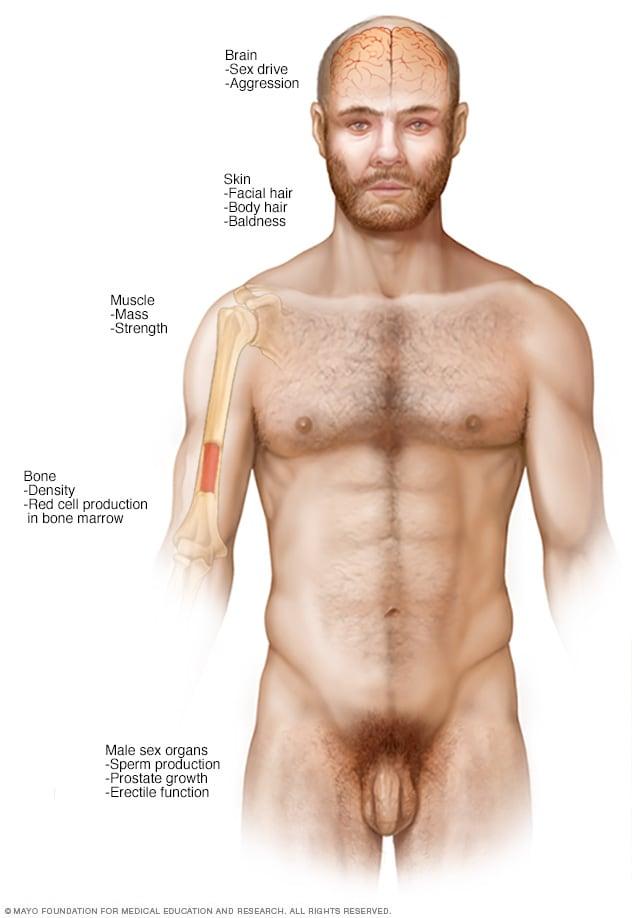
Moreover, testosterone is essential for maintaining hormonal balance within the body. It influences the production of other hormones, including estrogen, which is vital for overall health in both men and women. By restoring testosterone levels, individuals may experience a more stable hormonal environment, aiding in the management of not just metabolic syndrome, but also related conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. The potential effects of testosterone therapy on hormonal balance can be summarized as follows:
| Effect | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Increased testosterone | Improved mood and energy levels |
| Restored estrogen levels | Better cardiovascular and bone health |
| Enhanced hormonal regulation | Stabilized metabolic processes |
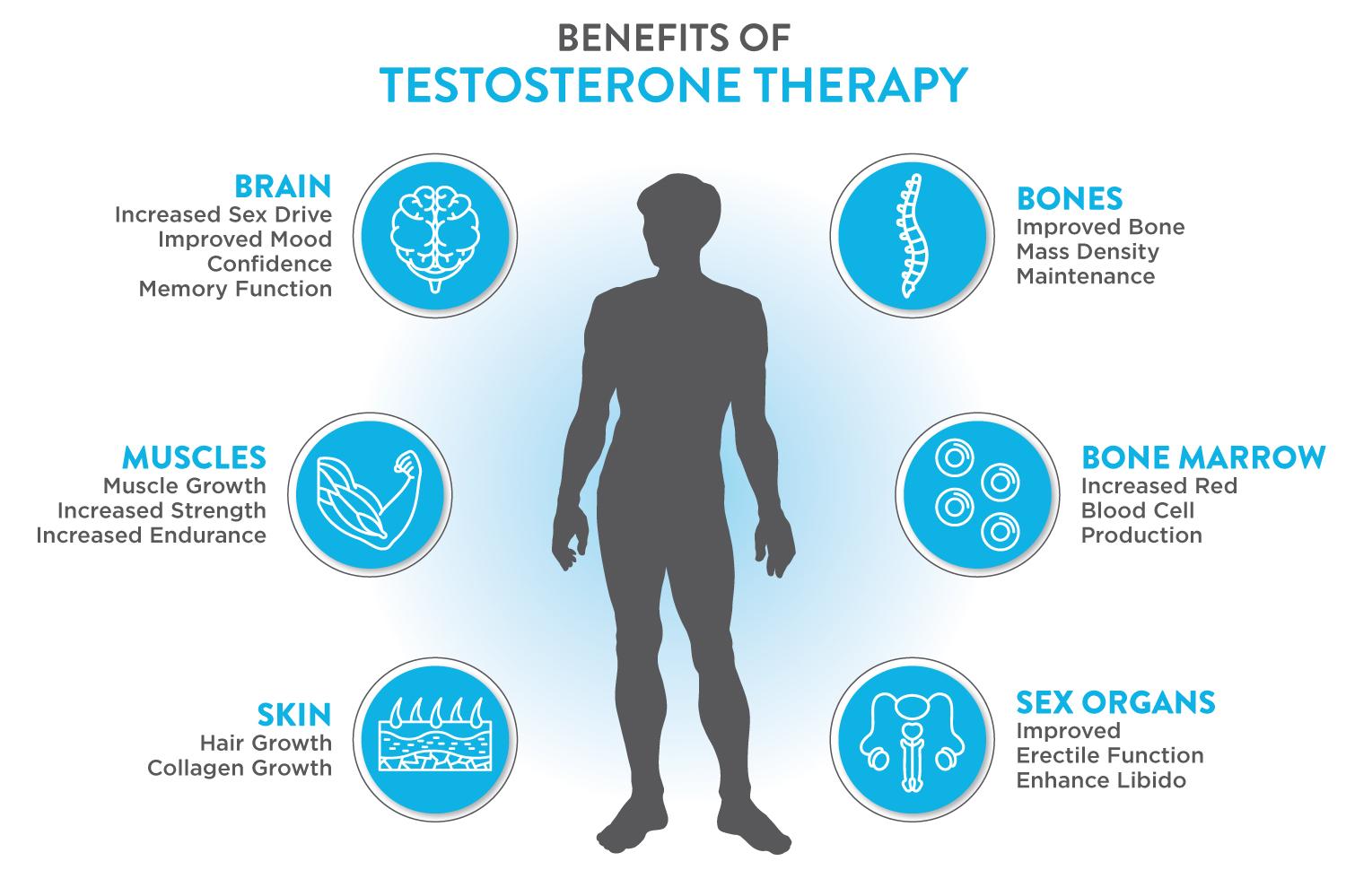
Evaluating the Benefits of Testosterone Therapy in Managing Metabolic Syndrome
Testosterone therapy has gained attention as a potential intervention for individuals grappling with metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions including obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and insulin resistance. A growing body of evidence suggests that testosterone replacement can help in addressing several key aspects of metabolic health. Among the notable benefits are:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Testosterone can enhance insulin sensitivity, reducing blood sugar levels and mitigating the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Reduced Body Fat: Men undergoing testosterone therapy often experience a reduction in abdominal fat, contributing to overall weight management.
- Boosted Muscle Mass: Increased testosterone levels can lead to greater muscle mass, which plays a crucial role in metabolism and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Enhanced Lipid Profile: Some studies indicate that testosterone therapy may aid in lowering triglycerides and increasing HDL cholesterol, thus promoting cardiovascular health.
Clinical studies have noted significant improvements in various metabolic parameters among patients receiving testosterone therapy compared to those who do not. These results underscore the potential of testosterone to act not just as a treatment for low testosterone levels but also as a valuable tool for managing the intricate challenges of metabolic syndrome. Below is a summary of key findings:
| Study | Duration | Metabolic Improvements |
|---|---|---|
| Study A | 12 Months | +20% Insulin Sensitivity |
| Study B | 6 Months | -15% Body Fat |
| Study C | 8 Months | +10% Muscle Mass |
Risks and Considerations: When Testosterone Therapy May Not Be Suitable
While testosterone therapy can offer significant benefits for individuals with metabolic syndrome, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Certain conditions may contraindicate its use, leading to potential risks that require careful consideration. For example, patients with a history of prostate cancer, polycythemia, or severe sleep apnea should proceed with caution. Additionally, those with untreated cardiovascular disease may experience exacerbated conditions, as testosterone can influence blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
It’s also crucial to evaluate hormonal levels and overall health before initiating therapy. The following factors should be taken into account:
- Aging-related hormonal decline: Natural fluctuations may not necessitate intervention.
- Weight status: Obesity can affect how testosterone is metabolized and may require lifestyle changes first.
- Existing comorbidities: Conditions like liver or kidney disease can complicate treatment.
- Family history: Inherited conditions, including clotting disorders, may heighten risk.
| Condition | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Prostate Issues | Monitor closely; therapy could worsen symptoms. |
| Heart Disease | Risk of increased heart events; evaluate thoroughly. |
| Liver/Kidney Dysfunction | May alter testosterone metabolism; assess renal and hepatic function. |
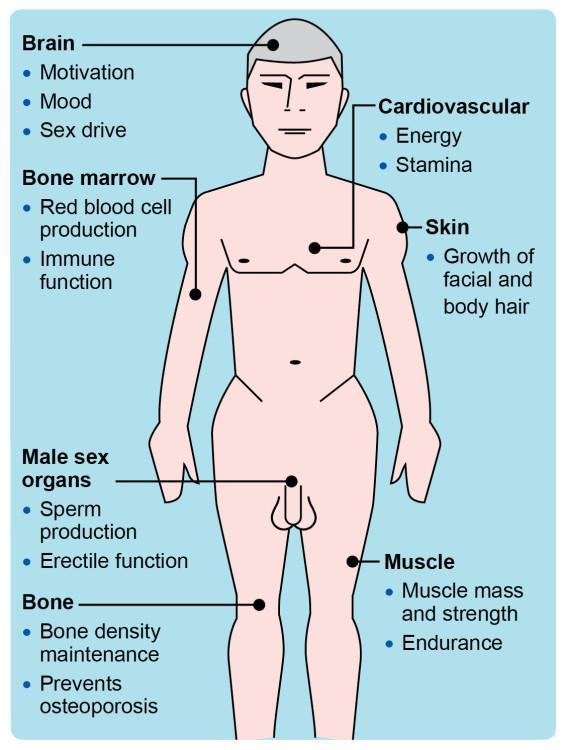
Integrating Lifestyle Changes with Testosterone Therapy for Optimal Results
To maximize the benefits of testosterone therapy, adopting complementary lifestyle changes is crucial. A balanced approach not only amplifies the effectiveness of treatment but also addresses underlying issues associated with metabolic syndrome. Key lifestyle modifications include:
- Nutrition: Focus on a diet rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise, incorporating both cardiovascular and strength-training workouts to support hormone balance.
- Stress Management: Implement mindfulness practices, such as meditation or yoga, to lower cortisol levels, which may interfere with testosterone efficacy.
- Sleep Hygiene: Prioritize quality sleep, aiming for 7–9 hours each night to promote optimal hormone production.
Moreover, understanding the synergistic relationship between testosterone therapy and lifestyle choices can further inform personal health strategies. Regular monitoring of health markers is essential, and a simple overview of critical indicators can facilitate better management:
| Health Indicator | Optimal Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Testosterone Levels | 300-1000 ng/dL | Regular testing is vital for dose adjustment. |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | 18.5-24.9 | Aim to maintain a healthy weight. |
| Blood Sugar Levels | 70-130 mg/dL (fasting) | Monitor levels to prevent insulin resistance. |
Monitoring and Measuring Success: Key Metrics in Therapy Progress
In managing the effects of testosterone therapy on metabolic syndrome, it’s crucial to identify and track specific metrics that reflect both physiological changes and subjective well-being. Important indicators to monitor include:
- Body Weight: Tracking fluctuations in weight can help gauge changes in fat mass and muscle composition.
- Waist Circumference: A decrease in waist size is often associated with improved metabolic health.
- Blood Pressure: Regular monitoring can reveal the therapy’s impact on cardiovascular risk factors.
- Blood Glucose Levels: Changes in fasting glucose can indicate how well the therapy is modulating insulin sensitivity.
- Lipid Profiles: Noting shifts in cholesterol and triglyceride levels is essential for cardiovascular health assessments.
Moreover, assessing quality of life and psychological well-being through standardized questionnaires can offer insights into the effectiveness of therapy. Consider integrating the following metrics into a comprehensive progress tracker:
| Metric | Baseline | 3-Month Follow-Up | 6-Month Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body Weight (kg) | 90 | 88 | 85 |
| Waist Circumference (cm) | 100 | 98 | 95 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 140 | 135 | 130 |
| Fasting Glucose (mg/dL) | 110 | 105 | 100 |
Future Perspectives: Emerging Research and Implications for Treatment Approaches
The burgeoning field of research around testosterone therapy highlights its promising role in managing metabolic syndrome, offering insights that could reshape conventional treatment paradigms. Emerging studies suggest that testosterone supplementation may improve insulin sensitivity, reduce visceral fat, and enhance lipid profiles, thereby addressing key components of metabolic syndrome. Clinical trials are beginning to reveal the biochemical pathways through which testosterone exerts these effects, including alterations in inflammatory markers and oxidative stress, which could pave the way for targeted therapies that focus explicitly on these pathways. As researchers delve deeper into these mechanisms, the hope is to define patient populations that may benefit most from testosterone therapy.
Future treatment approaches may also emphasize the importance of personalized medicine, taking into account individual hormonal profiles, comorbidities, and lifestyle factors. Strategies for implementation could encompass multifaceted interventions, integrating testosterone therapy with dietary modifications, exercise regimens, and other pharmacologic treatments. The potential for combination therapies could increase the efficacy of managing metabolic syndrome, yet they demand rigorous investigation. Continued research will be crucial in establishing standardized protocols and guidelines that ensure the safe and effective use of testosterone therapy, with an eye towards improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Q&A
Q&A: Unpacking Testosterone Therapy for Metabolic Syndrome
Q1: What is metabolic syndrome, and why is it a concern?
A1: Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. It typically includes increased blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels. As global obesity rates escalate, metabolic syndrome has emerged as a significant public health concern.
Q2: How does testosterone relate to metabolic syndrome?
A2: Testosterone plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions, including fat distribution, muscle mass, and insulin sensitivity. Research suggests a link between low testosterone levels and the risk of developing metabolic syndrome. Insufficient testosterone may exacerbate symptoms, contributing to weight gain and decreased muscle mass.
Q3: What are the potential benefits of testosterone therapy for individuals with metabolic syndrome?
A3: Testosterone therapy can lead to several promising outcomes for those with metabolic syndrome. These may include improvements in body composition, increased muscle strength, enhanced insulin sensitivity, and a reduction in visceral fat. Some studies also indicate potential improvements in cardiovascular health markers.
Q4: Who should consider testosterone therapy for metabolic syndrome?
A4: Testosterone therapy may be suitable for men diagnosed with low testosterone levels and symptoms of metabolic syndrome. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to assess individual risks, benefits, and treatment criteria. Women with metabolic syndrome might also experience hormonal imbalances, but testosterone therapy is less common and should be approached with caution.
Q5: Are there risks associated with testosterone therapy?
A5: Yes, like any medical treatment, testosterone therapy carries risks. Potential side effects may include increased risk of heart disease, sleep apnea, acne, and mood fluctuations. It’s crucial for individuals considering therapy to have a thorough discussion with their healthcare provider to weigh the benefits against the risks.
Q6: What methodologies are employed when administering testosterone therapy?
A6: Testosterone therapy can be administered through various methods, including injections, patches, gels, and pellets. Healthcare providers typically determine the most suitable method based on the patient’s lifestyle, preferences, and specific health considerations.
Q7: Can lifestyle changes complement testosterone therapy for managing metabolic syndrome?
A7: Absolutely! While testosterone therapy can be beneficial, it’s most effective when combined with lifestyle modifications. Emphasizing a balanced diet, regular physical activity, weight management, and stress reduction can significantly enhance overall health and potentially mitigate the effects of metabolic syndrome.
Q8: What’s the takeaway for someone curious about testosterone therapy and metabolic syndrome?
A8: The connection between testosterone levels and metabolic syndrome is an evolving area of research. While testosterone therapy may offer benefits for some individuals, it’s essential to approach the decision with careful consideration and guidance from healthcare professionals. Prioritizing a holistic approach that includes lifestyle adjustments can create a comprehensive strategy for managing metabolic syndrome effectively.
Future Outlook
the exploration of testosterone therapy as a potential intervention for metabolic syndrome unveils a complex interplay between hormones and health. While the promise of improved metabolic markers and enhanced quality of life is intriguing, the journey toward understanding its full impact is ongoing. As researchers delve deeper into the intricacies of testosterone’s role in metabolic health, it becomes evident that personalized approaches and careful monitoring will be crucial in harnessing its benefits while minimizing risks. Ultimately, the path forward involves collaboration among healthcare providers, researchers, and patients, fostering a holistic perspective that supports not just the individual, but the community at large in the fight against metabolic syndrome. As we stand at the crossroads of science and well-being, the future of testosterone therapy holds potential, inviting us to continue questioning, learning, and evolving in our quest for better health.









