Exploring the Role of Testosterone Therapy in Osteoporosis Management
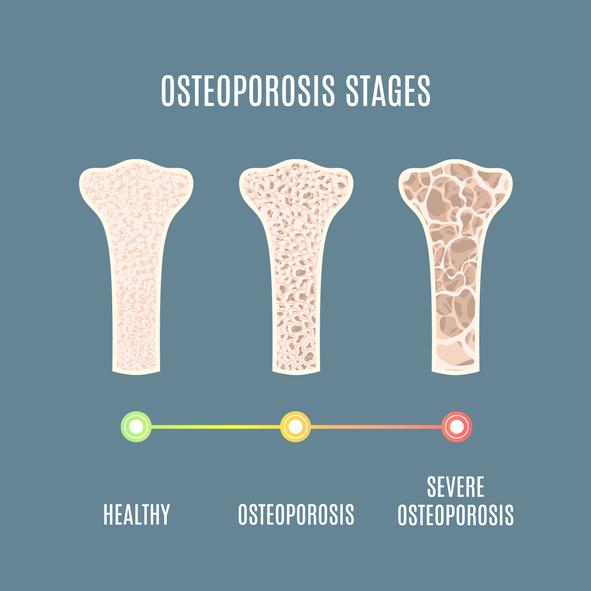
In the realm of bone health, osteoporosis stands out as a silent adversary, stealthily weakening bones and increasing the risk of fractures, particularly in older adults. Traditionally associated with women, this condition affects both genders, calling for a comprehensive understanding of its underlying causes and innovative treatment options. As researchers delve deeper into the intricate relationship between hormones and bone density, testosterone therapy has emerged as a focal point of interest, especially for men grappling with osteoporosis. This article aims to unpack the complexities of testosterone’s role in maintaining bone health, examining the potential benefits and considerations of hormone replacement therapy as a viable option in osteoporosis management. Join us as we navigate through the latest findings, expert insights, and the broader implications of testosterone therapy, shedding light on a path less traveled in the quest for stronger bones.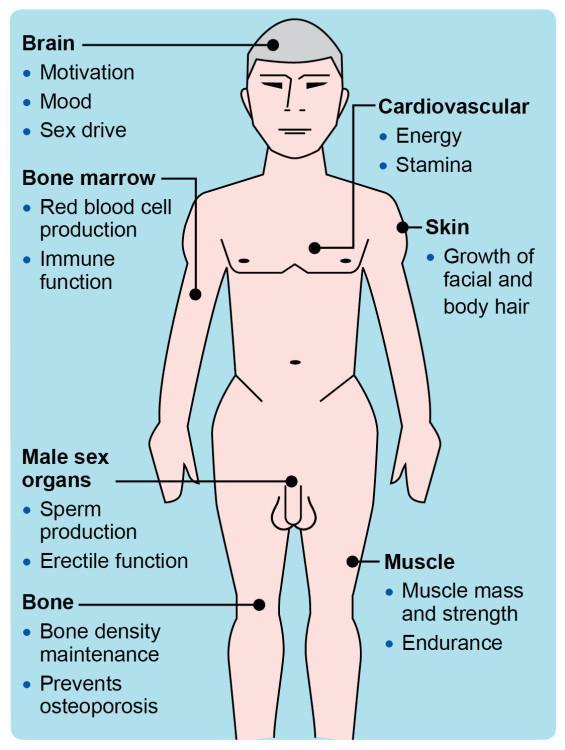
Understanding the Connection Between Testosterone and Bone Health
The intricate relationship between testosterone levels and bone health is an area of growing interest within the medical community. Testosterone plays a critical role in the maintenance of bone density, helping to prevent conditions such as osteoporosis. Research indicates that low testosterone levels can lead to diminished bone mass, which increases the risk of fractures and other skeletal complications. Here are some key points highlighting this connection:
- Bone Density: Testosterone is crucial for the bone remodeling process, promoting the activity of osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation.
- Osteoporosis Risk: Men with low testosterone face a higher likelihood of developing osteoporosis, making hormone levels a vital aspect of preventive care.
- Age Factor: Testosterone levels naturally decline with age, underscoring the importance of monitoring hormonal health in older males.
Moreover, the administration of testosterone therapy has shown promise in reversing the negative effects associated with low hormone levels. Studies have demonstrated that such treatments can enhance bone density and decrease fracture incidence among men diagnosed with osteoporosis. It’s essential to consider factors such as:
| Consideration | Importance |
|---|---|
| Timing of Therapy | Earlier intervention may yield better outcomes. |
| Dosing Precision | Optimal dosages can maximize benefits while minimizing risks. |
| Monitoring | Regular follow-ups to assess bone health and testosterone levels. |
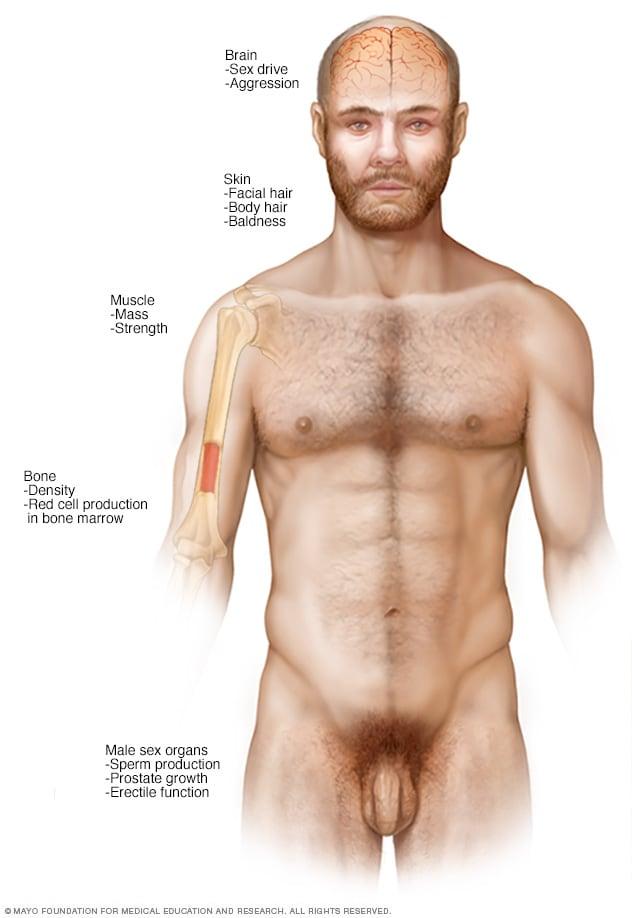
The Role of Testosterone Therapy in Osteoporosis Management
Testosterone therapy has emerged as a pivotal strategy in the management of osteoporosis, particularly among men facing hormone deficiencies. By facilitating an increase in bone mineral density, testosterone plays a crucial role in sustaining skeletal integrity. Its effects can be summarized as follows:
- Bone Mass Improvement: Testosterone stimulates osteoblast activity, enhancing bone formation.
- Calcium Regulation: It aids in maintaining calcium balance, essential for healthy bone metabolism.
- Muscle Strength Boost: Improved muscle mass contributes to better physical stability, reducing fracture risk.
Clinical studies indicate that testosterone replacement can significantly reduce the incidence of fractures in older men with low testosterone levels. However, it is vital to consider the therapy’s multifaceted aspects, including:
- Individual Responsiveness: Not all patients respond uniformly; tailoring therapy is essential.
- Monitoring Side Effects: Regular assessments are crucial to mitigate potential adverse effects.
- Comprehensive Treatment Plan: Combining testosterone therapy with other osteoporosis interventions can yield optimal results.
Evaluating the Risks and Benefits of Hormonal Treatments
When considering testosterone therapy as a treatment for osteoporosis, it’s vital to weigh both its potential benefits and associated risks carefully. Among the most commonly cited benefits are:
- Bone Density Improvement: Testosterone can enhance bone mineral density, reducing the risk of fractures.
- Muscle Mass Increase: Therapy may contribute to increased muscle strength, further supporting bone health.
- Improved Mood and Energy Levels: Some patients report enhanced well-being, which may encourage physical activity.
Conversely, the treatment carries certain risks that should not be overlooked. These may include:
- Cardiovascular Issues: There’s a potential for heightened blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Excess testosterone can lead to negative effects such as mood swings or infertility.
- Prostate Health Concerns: For men, there are concerns about the potential acceleration of prostate cancer.
| Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|
| Bone Density Improvement | Cardiovascular Issues |
| Increased Muscle Mass | Hormonal Imbalance |
| Enhanced Mood | Prostate Health Concerns |
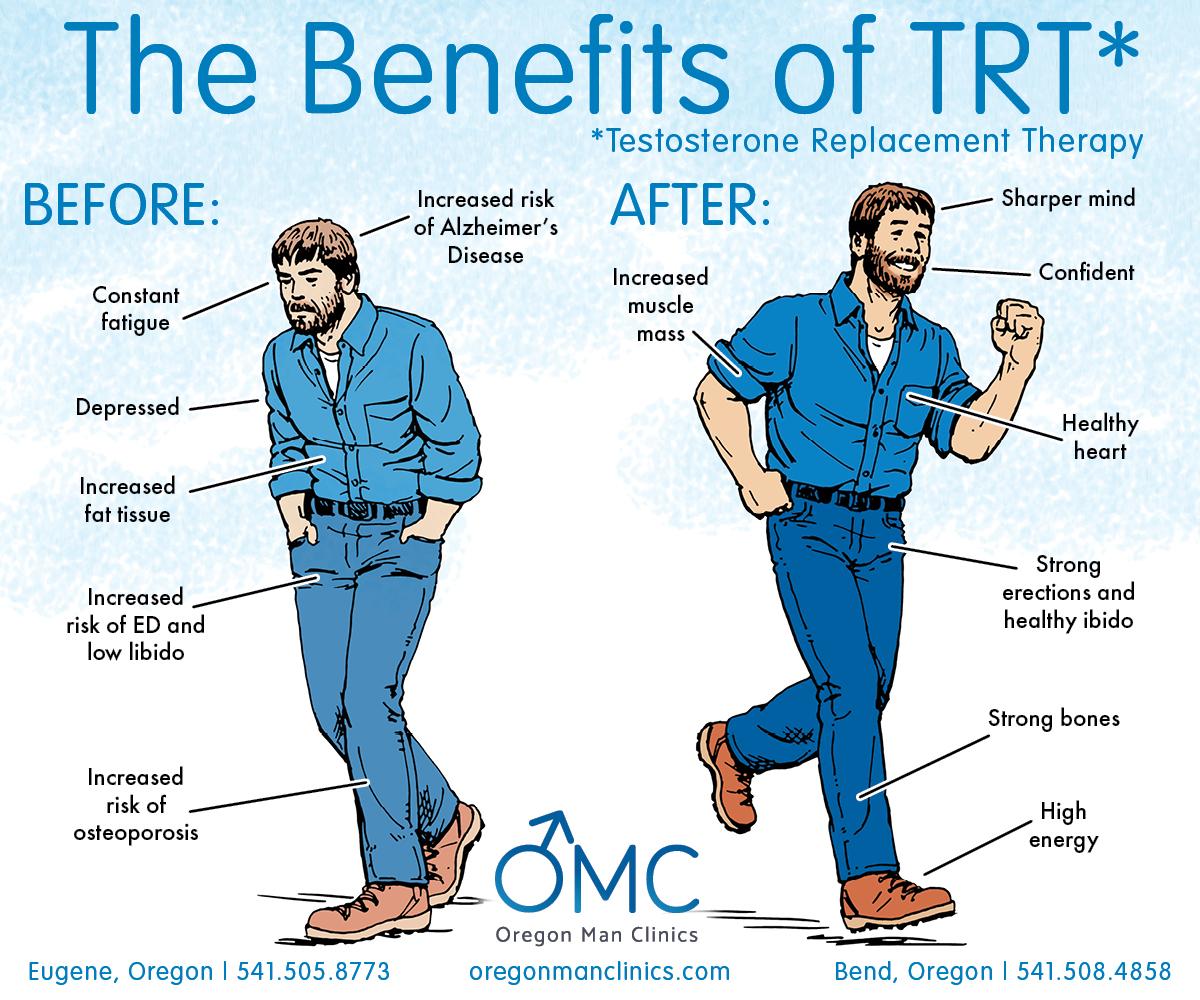
Tailoring Testosterone Therapy for Individual Patient Needs
In the realm of osteoporosis treatment, the significance of individualizing testosterone therapy cannot be overstated. Many factors must be considered to create a tailored approach that maximizes benefits while minimizing risks. Physicians often assess the patient’s age, baseline hormone levels, lifestyle choices, and comorbid conditions. By focusing on these distinct patient characteristics, clinicians can determine appropriate dosages and delivery methods. Ensuring frequent monitoring of hormone levels and bone density is essential for sufficient adjustments and achieving optimal outcomes.
Furthermore, the choice of testosterone formulation plays a pivotal role in addressing the needs of each patient. Options range from injections and gels to implants, each with unique pharmacokinetics and patient experiences. Weight loss, muscle mass increase, and improved bone density are some of the anticipated outcomes of well-structured therapy. A table summarizing distinctive treatment formulations may serve as a quick reference for clinicians to decide on the best approach tailored to their patients’ requirements:
| Formulation | Administration Method | Frequency | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injectable | Intramuscular | Every 2-4 weeks | Rapid increases in testosterone levels |
| Gel | Topical | Daily | Steady hormone release |
| Implant | Subcutaneous | Every 3-6 months | Long-term stabilization of hormone levels |
Monitoring Bone Density: Key Considerations for Therapy Success
Monitoring bone density is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of testosterone therapy in managing osteoporosis. Regular assessments can help gauge treatment efficacy and ensure that the patient’s bone mineral density (BMD) improves over time. Key strategies to consider include:
- Frequency of Testing: Baseline BMD should be evaluated at the start of therapy, followed by reassessments every 1 to 2 years depending on initial results.
- Utilizing DXA Scans: Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans are the gold standard for measuring bone density and can pinpoint areas of concern.
- Tracking Hormonal Levels: Alongside monitoring BMD, it is crucial to regularly check testosterone levels to ensure they are within therapeutic ranges.
- Assessing Risk Factors: Patients should be evaluated for other osteoporosis risk factors like age, weight, and family history, which may influence treatment decisions.
Incorporating a multidisciplinary approach can further enhance bone health management. Collaborations between endocrinologists, primary care physicians, and nutritionists can provide a comprehensive overview of patient needs. To optimize therapy success, consider tracking the following parameters:
| Parameter | Importance |
|---|---|
| Bone Mineral Density (BMD) | Defines the severity of osteoporosis. |
| Testosterone Levels | Directly correlates with treatment responsiveness. |
| Calcium Intake | Supports overall bone health. |
| Vitamin D Levels | Enhances calcium absorption for better bone density. |
Lifestyle Factors That Complement Testosterone Therapy
Integrating testosterone therapy with a well-rounded lifestyle can enhance its effectiveness significantly. Nutrition, for instance, plays a pivotal role. Consuming a diet rich in essential nutrients can support bone health and overall hormonal balance. Focus on including:
- Calcium-rich foods: Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods help strengthen bones.
- Vitamin D: Sources like fatty fish and egg yolks aid in calcium absorption.
- Healthy fats: Incorporate avocados, nuts, and olive oil to promote testosterone production.
Alongside diet, physical activity is crucial. Regular exercise not only helps in building bone density but also boosts testosterone levels. Consider engaging in:
- Resistance training: Lifting weights or bodyweight exercises can significantly improve muscle mass and bone strength.
- Aerobic exercise: Activities like running or swimming enhance cardiovascular health, which can support overall well-being.
- Flexibility and balance practices: Yoga or tai chi can reduce fall risk, which is especially important for those with osteoporosis.
To visualize the interplay of these factors, consider the following table:
| Factor | Impact on Health |
|---|---|
| Nutrition | Supports bone density and hormonal balance |
| Resistance Training | Increases muscle and bone strength |
| Aerobic Exercise | Enhances cardiovascular health and wellness |
| Flexibility Practices | Reduces risk of falls and injuries |
Future Directions in Osteoporosis Treatment and Research
As modern medicine evolves, innovative approaches in osteoporosis treatment and research are gaining traction, especially regarding the potential role of testosterone therapy. This therapeutic option holds promise for addressing not only bone density loss but also associated conditions such as frailty and sarcopenia. Research efforts are currently focused on understanding how testosterone influences bone remodeling and the synergistic effects when combined with other treatments. The implications of these studies may reshape clinical guidelines and patient management in the coming years:
- Refining dosage protocols to optimize treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects.
- Investigating genetic factors that may influence patient responses to testosterone therapy.
- Exploring combination therapies with bisphosphonates or other anabolic agents.
- Establishing long-term outcomes on strength, mobility, and quality of life in patients receiving testosterone.
Furthermore, the landscape of osteoporosis research is increasingly incorporating multi-disciplinary approaches, combining endocrinology, geriatrics, and pharmacology. Collaborative studies are likely to lead to more comprehensive treatment frameworks that take into account patients’ hormonal profiles alongside their osteoporosis risk factors. The following table summarizes key areas of future exploration:
| Research Area | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Testosterone dosage optimization | Improved patient outcomes |
| Genetic influence on therapy | Personalized treatment plans |
| Combination therapies | Enhanced efficacy |
| Long-term health outcomes | Better quality of life assessments |
Q&A
Q&A: Testosterone Therapy for Osteoporosis
Q1: What is osteoporosis, and why is it a concern for men’s health?
A1: Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones that are more susceptible to fractures. Traditionally viewed as a women’s health issue, osteoporosis is increasingly recognized in men, especially as they age. Factors such as decreased hormone levels, including testosterone, can significantly contribute to bone density loss, making it a critical health concern for men in their later years.
Q2: How does testosterone influence bone health?
A2: Testosterone plays an essential role in maintaining bone density. It helps to stimulate bone formation and mineralization, which are crucial processes for keeping bones strong. When testosterone levels drop, especially during andropause, men may experience an accelerated loss of bone density, increasing their risk for osteoporosis and related fractures.
Q3: What is testosterone therapy, and how does it work?
A3: Testosterone therapy involves administering testosterone to individuals with low testosterone levels, often through injections, patches, or gels. By restoring healthier testosterone levels, the treatment aims to improve bone density, enhance overall well-being, and reduce the risk of osteoporosis-related fractures.
Q4: Is testosterone therapy suitable for all men with osteoporosis?
A4: Not necessarily. Testosterone therapy is typically recommended for men diagnosed with hypogonadism (clinically low testosterone levels). A thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider is essential to determine if testosterone therapy is appropriate, as it may not be suitable for men with normal testosterone levels or certain medical conditions.
Q5: What are the potential benefits of testosterone therapy for osteoporosis?
A5: Potential benefits of testosterone therapy for men with osteoporosis include an increase in bone mineral density, a reduction in fracture risk, improved muscle mass, and enhanced mood and energy levels. These benefits can significantly contribute to an improved quality of life.
Q6: Are there risks associated with testosterone therapy?
A6: Yes, while testosterone therapy offers several benefits, it also comes with potential risks. These may include increased risk of cardiovascular events, sleep apnea, and prostate health issues. It’s important for men considering therapy to discuss these risks with their healthcare provider and undergo regular monitoring during treatment.
Q7: What other treatments are available for osteoporosis in men?
A7: Aside from testosterone therapy, there are other treatment options for osteoporosis in men, including bisphosphonates, denosumab, and teriparatide. Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, regular weight-bearing exercise, and avoiding smoking can also help maintain bone health.
Q8: How can men proactively manage their bone health?
A8: Men can take several steps to promote good bone health. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and monitoring bone density can all contribute to reducing the risk of osteoporosis. If experiencing symptoms of low testosterone, such as fatigue or decreased libido, seeking medical advice is crucial for timely intervention.
Q9: What should men consider when contemplating testosterone therapy for osteoporosis?
A9: Men should weigh the potential benefits against the risks and discuss their specific health circumstances with their healthcare provider. Understanding personal health history, family history of osteoporosis, and lifestyle factors will help inform the decision-making process regarding testosterone therapy.
Q10: Where can men find more information about testosterone therapy and osteoporosis?
A10: Men seeking more information can consult their healthcare providers, visit reputable medical websites, and consider resources from organizations dedicated to bone health, such as the National Osteoporosis Foundation. Education is key, and empowering oneself with knowledge will aid in making informed health decisions.
Wrapping Up
the exploration of testosterone therapy as a potential treatment for osteoporosis opens new avenues for both research and patient care. As we unravel the complexities of hormonal influences on bone health, it becomes clear that a multi-faceted approach is necessary to combat this silent yet impactful condition. While the promise of testosterone therapy holds merit, it is essential to weigh its benefits against potential risks and to consider it as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. As science continues to evolve, so too will our understanding of osteoporosis and the role hormones play in maintaining bone density. For those affected, staying informed and engaged with healthcare professionals will be crucial in navigating this promising, yet intricate landscape. Healing, as we know, is a journey—one that we embark upon with both caution and hope.