Title: Rediscovering Vitality: The Rise of Testosterone Therapy for Post-Menopausal Men
In the complex landscape of human health, hormonal changes often remain shrouded in mystery, particularly when it comes to the effects of aging on men’s bodies. While much attention has traditionally been given to women navigating the tumultuous waters of menopause, an equally significant shift occurs in men as they transition into their later years. Enter testosterone therapy—a treatment that has emerged from the shadows, promising a potential revival of vitality for post-menopausal men. As the understanding of hormonal balance evolves, this article explores the intricacies of testosterone therapy, its implications for health and well-being, and the nuanced narratives surrounding this transformative option. Through a lens of scientific inquiry and personal stories, we will uncover the relevance of testosterone therapy for those seeking to embrace life’s later chapters with renewed vigor and purpose.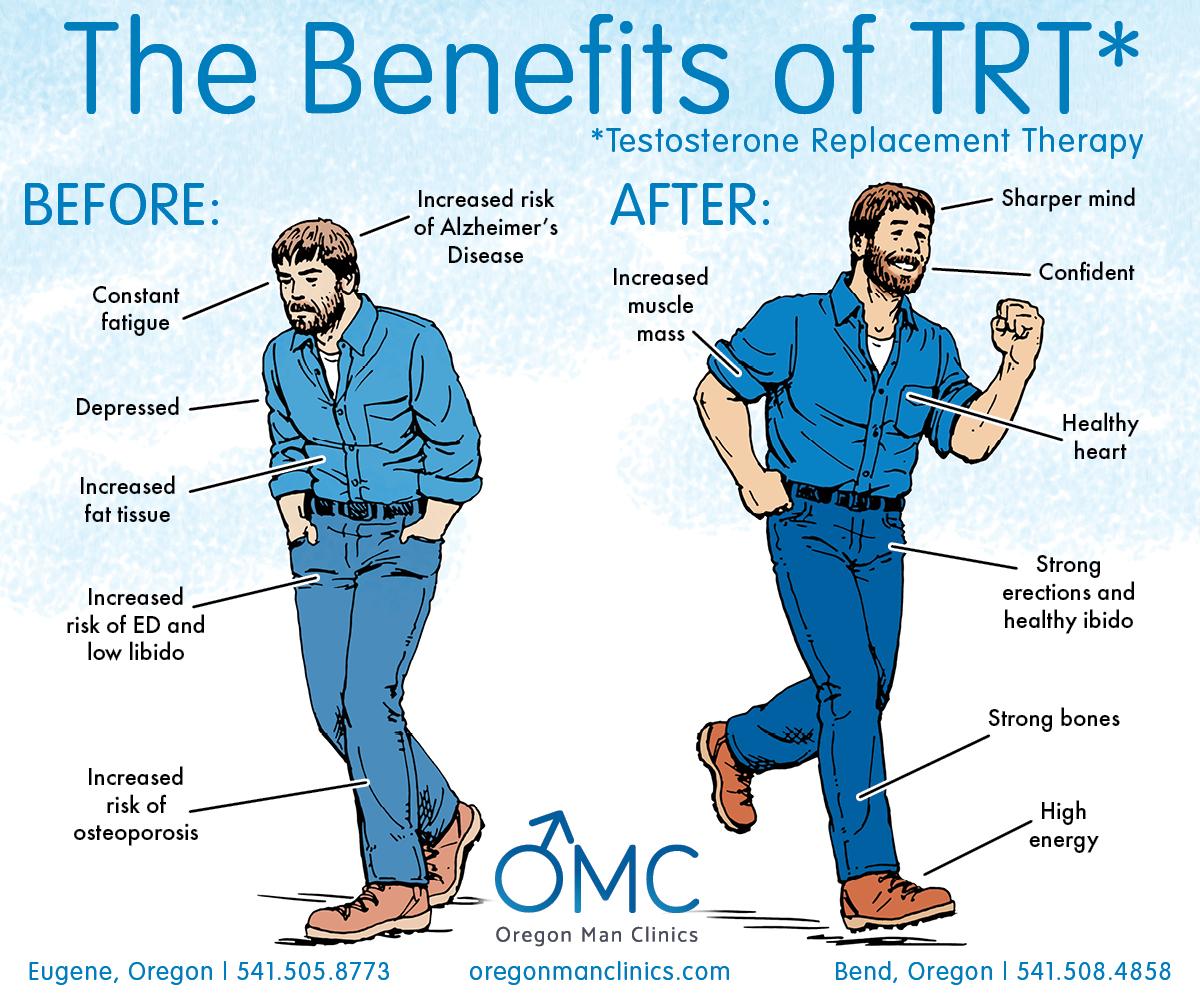
Understanding Testosterone Therapy in Post-Menopausal Men
Testosterone therapy is gaining attention as a viable option for men after menopause, a term often associated with women but equally relevant in discussing male hormonal changes. As men age, particularly after reaching their 50s and 60s, there is a natural decline in testosterone levels, which can lead to a variety of symptoms such as fatigue, decreased libido, mood changes, and loss of muscle mass. Understanding how testosterone therapy works can help men make informed decisions about their health. By restoring testosterone levels to a more youthful state through various administration methods—such as injections, patches, gels, or pellets—many men experience an improvement in energy, enhanced sexual function, and an overall better quality of life.
The therapeutic benefits of testosterone therapy, however, come with a range of considerations. Potential risks include cardiovascular issues, sleep apnea, and prostate health concerns. It is crucial for any man considering this treatment to engage in a thorough discussion with healthcare providers about personal health history and risk factors. Regular monitoring is key to ensuring that the therapy is both safe and effective. Factors to contemplate when considering testosterone therapy include:
- Current testosterone levels: A comprehensive blood test is essential.
- Health screenings: Regular check-ups can help identify any existing conditions.
- Discussion of lifestyle changes: Diet and exercise may also significantly impact overall hormonal balance.
| Testosterone Therapy Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Injections | Fast acting, can deliver high doses. | Pain at the injection site, need for regular visits. |
| Patches | Convenient and easy to apply. | Skin irritation, can fall off. |
| Gels | Simple to use and absorb quickly. | Risk of transfer to others, messier application. |
| Pellets | Long-lasting results, requires fewer applications. | Requires minor surgical procedure for insertion. |
Navigating the Signs and Symptoms of Low Testosterone Levels
Detecting low testosterone levels can be a nuanced process, as its signs and symptoms often overlap with other health conditions. Common indicators include:
- Reduced libido or sexual desire
- Fatigue and decreased energy levels
- Declining strength and muscle mass
- Weight gain, particularly around the abdomen
- Depressive moods or changes in emotional state
It’s crucial for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek advice from healthcare professionals who specialize in hormone therapy. Comprehensive evaluations often involve blood tests to assess hormone levels, alongside considering individual medical history. Below is a concise table summarizing the potential impacts of low testosterone:
| Impact of Low Testosterone | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Changes | Loss of muscle mass, increased body fat |
| Mental Health | Increased feelings of fatigue or depression |
| Reproductive Health | Decreased libido and erectile dysfunction |
| Bone Density | Risk of osteoporosis and fractures |
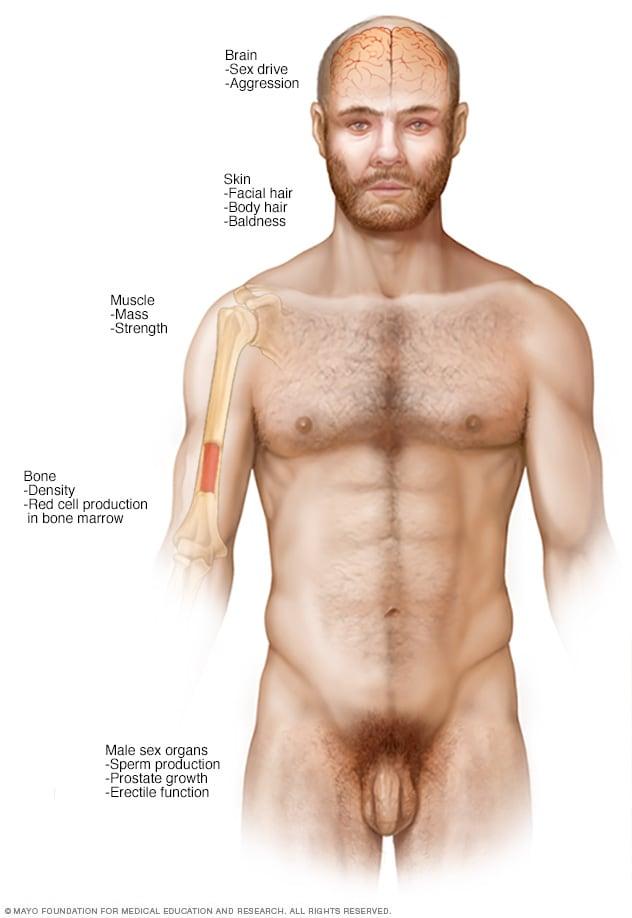
Clinical Benefits of Testosterone Replacement in Aging Men
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) offers a multitude of clinical benefits for aging men that extend beyond mere hormone replenishment. Research indicates that maintaining optimal testosterone levels can lead to improvements in muscle mass, bone density, and overall physical vitality. As men age, testosterone levels may decline, resulting in symptoms such as fatigue, reduced libido, and diminished cognitive function. By addressing these hormonal deficits, TRT not only aids in restoring physical performance but also promotes enhanced energy levels and improved mood stability.
Furthermore, the implications of testosterone therapy reach into more specific health improvements. Studies have highlighted its role in reducing the risk of conditions linked to low testosterone levels, including diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The table below summarizes key health markers positively affected by testosterone replacement therapy:
| Health Marker | Effects of TRT |
|---|---|
| Muscle Mass | Increased strength and lean mass |
| Bone Density | Improved bone strength |
| Cardiovascular Health | Reduced arterial stiffness |
| Mood | Decreased anxiety and depression |
| Cognitive Function | Enhanced focus and memory |
The multifaceted benefits of TRT underscore its significance in enhancing the quality of life for men facing age-related hormonal declines. By fostering an understanding of these advantages, men can engage in informed discussions with their healthcare providers, paving the way for healthier, more active lifestyles.
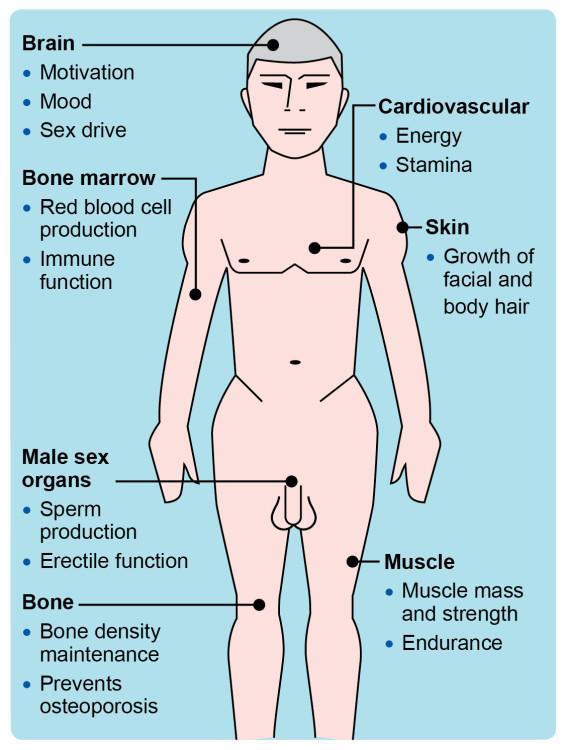
Evaluating Different Methods of Testosterone Administration
The administration of testosterone can be approached through various methods, each offering unique advantages and considerations. Injectable testosterone comes in two main forms: intramuscular and subcutaneous injections. Intramuscular injections are generally administered every two to four weeks, resulting in stable blood levels, albeit with potential discomfort and the need for professional application. Alternatively, subcutaneous injections can often be performed at home and may provide a more favorable experience for some patients. Another commonly used method is transdermal delivery, which includes patches and gels that allow testosterone to be absorbed through the skin. This method offers the convenience of daily application and steady hormone levels but may come with skin irritation and the risk of transferring the hormone to others.
Moreover, oral testosterone options, while less conventional due to concerns about liver toxicity, have been modernized with recent formulations aimed at minimizing these risks. Pellet therapy is another attractive option; small pellets are implanted under the skin and release testosterone over several months, offering sustained hormone levels without the need for frequent dosing. To assist in decision-making regarding the most suitable administration method, the following factors should be considered:
| Method | Frequency | Convenience | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injectable (IM/SubQ) | Every 2-4 weeks | Moderate | Pain, bruising |
| Transdermal (Patch/Gel) | Daily | High | Skin irritation |
| Oral | Daily | High | Liver concerns |
| Pellet Therapy | Every 3-6 months | High | Surgical risks |
Considerations and Risks Involved in Hormonal Therapy
When considering testosterone therapy for post-menopausal men, it is essential to weigh the potential benefits against various risks. While the therapy may offer improvements in mood, muscle mass, and overall energy levels, it is not devoid of drawbacks. Common risks associated with testosterone therapy include:
- Cardiovascular issues: Increased risk of heart attacks or strokes, especially in older adults.
- Hormonal imbalances: Potential development of gynecomastia or other hormonal changes.
- Sleep apnea: Worsening of existing sleep apnea symptoms.
- Prostate health: Risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia or changes in prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels.
Moreover, the long-term effects of testosterone replacement therapy are still being studied. Regular monitoring and screening are crucial to mitigate these risks. Healthcare providers should consider factors such as:
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Age | Older patients may have a higher risk of adverse effects. |
| Existing conditions | Pre-existing cardiovascular or prostate issues need thorough evaluation. |
| Dosage | Aim for the lowest effective dose to minimize risks. |
| Monitoring | Regular blood tests and physical exams to track therapy effects. |
Tailoring Treatment Plans for Individual Needs and Health Conditions
In medical practice, it’s essential to recognize that no two patients are alike, especially when addressing hormone-related conditions such as testosterone deficiency in post-menopausal men. Each treatment plan must be thoughtfully crafted, taking into account individual health history, lifestyle factors, and specific symptoms. Factors to consider include:
- Age and Overall Health: Comprehensive assessments help determine the severity of testosterone deficiency and guide therapeutic decisions.
- Comorbid Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular issues, or obesity can impact treatment efficacy and safety.
- Personal Preferences: Patient comfort with various treatment methods, such as injections, gels, or pellets, should inform the approach.
- Monitoring and Adjustments: Regular follow-ups are crucial for adjusting dosages and minimizing side effects.
Furthermore, collaborating with patients to outline their goals for therapy can enhance treatment satisfaction. An adaptable approach often includes educational resources to empower patients, allowing them to take an active role in their health decisions. The following table illustrates potential strategies used in tailoring therapy:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Assessment | Comprehensive evaluation to identify testosterone levels and health status. |
| Customized Dosing | Personalized dosage based on individual response and lifestyle factors. |
| Multi-Disciplinary Approach | Involving specialists (endocrinologists, nutritionists) for holistic care. |
| Patient Education | Informing patients about potential benefits and risks of therapy. |
The Role of Lifestyle Changes in Enhancing Therapy Outcomes
When seeking to improve the effects of testosterone therapy in post-menopausal men, integrating lifestyle changes can amplify results significantly. Key adjustments can target various aspects of well-being, leading to a more holistic approach to health. Consider adopting a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, including:
- Lean Proteins – Found in poultry, fish, and legumes, they support muscle maintenance.
- Healthy Fats – Incorporate sources like avocados and nuts to promote heart health.
- Whole Grains – Choose brown rice, quinoa, and oats for sustained energy levels.
- Fruits and Vegetables - Packed with vitamins and antioxidants for overall wellness.
Moreover, physical activity is crucial in this transformative journey. Engaging in regular exercise not only boosts mood but also enhances metabolic efficiency, helping to optimize testosterone levels in conjunction with therapy. Effective strategies include:
- Strength Training – Lifting weights improves muscle mass and metabolism.
- Cardiovascular Workouts – Activities like running or cycling enhance cardiovascular health.
- Flexibility Exercises – Yoga or stretching promotes better mobility and reduces stress.
Implementing these lifestyle modifications can lead to a more profound therapeutic response, allowing individuals to regain vitality and improve their quality of life.
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Testosterone Therapy for Post-Menopausal Men
Q1: What is testosterone therapy, and why is it becoming more discussed for men, specifically post-menopausal?
A1: Testosterone therapy is a medical treatment aimed at increasing testosterone levels in men who have lower than normal levels, often due to age or hormonal changes. The term “post-menopausal men” might sound unusual, but as men age, their testosterone levels gradually decline, similar to how women experience hormonal changes during menopause. This can lead to symptoms like fatigue, decreased libido, and mood changes. Recent discussions center on the potential benefits and risks of therapy to address these symptoms.
Q2: What are the common symptoms that may lead a post-menopausal man to consider testosterone therapy?
A2: Men experiencing low testosterone may notice a variety of symptoms, such as fatigue, reduced muscle mass, increased body fat, mood swings or depression, decreased sexual desire, and challenges with concentration. Recognizing these symptoms can motivate individuals to explore options like testosterone therapy to improve their overall quality of life.
Q3: Who should consider testosterone therapy, and what factors might influence this decision?
A3: Testosterone therapy is typically considered for men who have clinically low testosterone levels confirmed by blood tests, accompanied by relevant symptoms. Factors influencing the decision include age, overall health, lifestyle, and the presence of pre-existing conditions such as heart disease or prostate issues. A thorough consultation with a healthcare provider is essential, as they can help evaluate the risks and benefits based on individual circumstances.
Q4: What are the potential benefits of testosterone therapy for post-menopausal men?
A4: Potential benefits of testosterone therapy can include improved energy levels, enhanced mood, increased libido, and better muscle strength. Some studies suggest it may contribute to improved bone density and a reduction in fat mass. This could help post-menopausal men regain a sense of vitality and well-being, allowing them to engage more fully in their lives.
Q5: Are there risks associated with testosterone therapy that men should be aware of?
A5: Yes, there are risks associated with testosterone therapy. Potential side effects may include acne, sleep apnea, increased risk of blood clots, and, in some cases, prostate growth or cancer. It’s vital for men to discuss these risks with their healthcare provider, who can monitor their condition and adjust treatment as necessary.
Q6: How is testosterone therapy administered, and what should men expect during treatment?
A6: Testosterone therapy can be administered in several ways, including injections, gels, patches, and pellets inserted under the skin. The choice of method depends on personal preference and medical advice. Men should expect regular check-ups, including blood tests to monitor testosterone levels and overall health. Adjustments to dosage may be needed based on how they respond to the therapy.
Q7: Is testosterone therapy a long-term solution or just a temporary fix?
A7: The duration of testosterone therapy can vary. Some men may find long-term benefits and continue treatment for years, while others may only need it temporarily to manage specific symptoms. It is crucial to have open discussions with a healthcare provider regarding long-term plans and the possibility of tapering off therapy if appropriate.
Q8: Can lifestyle changes complement testosterone therapy for better results?
A8: Absolutely! Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and adequate sleep can enhance the efficacy of testosterone therapy. Incorporating healthy habits can also address some symptoms related to low testosterone, offering a more holistic approach to health and well-being.
Q9: How can a post-menopausal man initiate the conversation about testosterone therapy with his doctor?
A9: The first step is to schedule an appointment and express concerns about symptoms that may be affecting quality of life. Providing specific examples, such as changes in energy levels or mood, helps initiate a more in-depth discussion. Men should feel empowered to ask questions about testosterone therapy and share their desire for a better understanding and management plan for their health.
Q10: what should men remember about testosterone therapy for post-menopausal conditions?
A10: Testosterone therapy can be a beneficial option for men experiencing the effects of declining testosterone levels. However, it requires careful consideration, a tailored approach, and ongoing communication with healthcare providers. By being informed and proactive, men can make decisions that align with their health goals and improve their well-being as they navigate the changes associated with aging.
Wrapping Up
As we navigate the evolving landscape of hormone therapy, the discussion surrounding testosterone replacement for post-menopausal men reveals both promise and complexity. While the potential benefits—ranging from enhanced vitality to improved mood—are compelling, it is imperative to approach this treatment with careful consideration and guidance from healthcare professionals. Each individual’s needs and circumstances vary, making personalized care essential.
In the quest to reclaim vigor in the later stages of life, the key lies in informed decision-making, open dialogue, and thorough medical evaluation. By melding the wisdom of science with the artistry of personal health, we can illuminate a path that honors both the challenges and opportunities that come with aging. As we continue to pierce the myths and unveil the truths surrounding testosterone therapy, let us remain dedicated to fostering well-being in what can be the most fulfilling years of our lives.










