In the complex tapestry of human health, the intricate interplays of hormones often tell stories that transcend their biological roots, weaving through realms of lifestyle, disease, and treatment. Among these chemical messengers, testosterone—a hormone traditionally associated with masculinity—has emerged as a focal point in the ongoing battle against type 2 diabetes, a condition that affects millions globally. As researchers delve deeper into the connections between hormonal balance and metabolic health, testosterone therapy has sparked curiosity and debate. Could this treatment offer a new lifeline for those grappling with insulin resistance and its myriad complications? This article explores the evolving landscape of testosterone therapy, examining its potential benefits, the science backing its use, and the crucial considerations for patients and healthcare practitioners navigating this promising yet nuanced approach to diabetes management. Join us as we uncover the relationship between testosterone and type 2 diabetes, shedding light on how this hormone could shape the future of diabetes care.
Understanding the Connection Between Testosterone and Insulin Sensitivity
Testosterone plays a critical role in regulating various metabolic functions, particularly in men. Research has shown that low levels of this hormone are associated with decreased insulin sensitivity, which can lead to complications in individuals with type 2 diabetes. When testosterone levels are optimized, it can result in improved glucose metabolism, reduced insulin resistance, and better overall glycemic control. This connection suggests that testosterone therapy might not only address hormonal deficiencies but could also serve as a pivotal adjunct treatment for managing type 2 diabetes.
The mechanisms behind this relationship are multifaceted. Testosterone enhances muscle mass, which in turn improves glucose uptake and utilization. Additionally, it influences fat distribution, leading to a decrease in visceral fat, known to be closely associated with insulin resistance. Here are some key aspects of the connection:
- Enhanced Muscle Insulin Sensitivity: Increased muscle mass improves insulin response.
- Fat Distribution: Testosterone helps regulate fat distribution, reducing abdominal fat.
- Glucose Metabolism: Optimized testosterone levels can enhance glucose metabolism pathways.
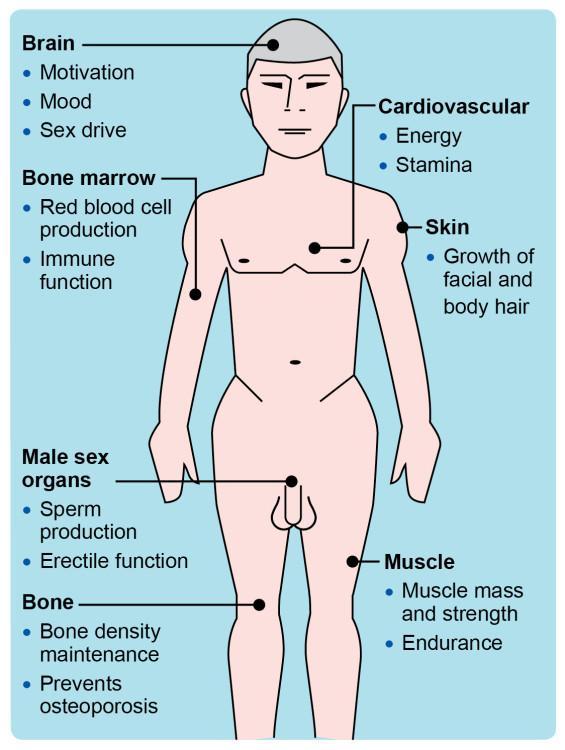
Exploring the Benefits of Testosterone Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Management
Testosterone therapy has emerged as a potential ally in the management of type 2 diabetes, particularly for men whose testosterone levels are diminished. Research indicates that low testosterone can negatively impact insulin sensitivity, leading to greater difficulties in glucose metabolism. By introducing testosterone therapy, patients may experience several significant benefits, including:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Higher testosterone levels can enhance the body’s ability to utilize insulin effectively.
- Weight Management: Testosterone therapy may aid in reducing visceral fat, which is often associated with insulin resistance.
- Increased Energy Levels: Patients often report higher energy levels, facilitating more active lifestyles and better adherence to recommended exercise regimens.
Furthermore, testosterone therapy has been linked to improved mood and overall quality of life. Depression and fatigue are common among those with type 2 diabetes, which may further complicate disease management. By addressing these psychological aspects, men may find it easier to engage in healthier habits. A quick overview of the impact of testosterone therapy on various parameters related to type 2 diabetes management can be outlined as follows:
| Parameter | Before Therapy | After Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Testosterone Levels | Low | Normal |
| Insulin Sensitivity | Low | Improved |
| Body Fat Percentage | High | Reduced |
| Energy Levels | Fatigued | Boosted |
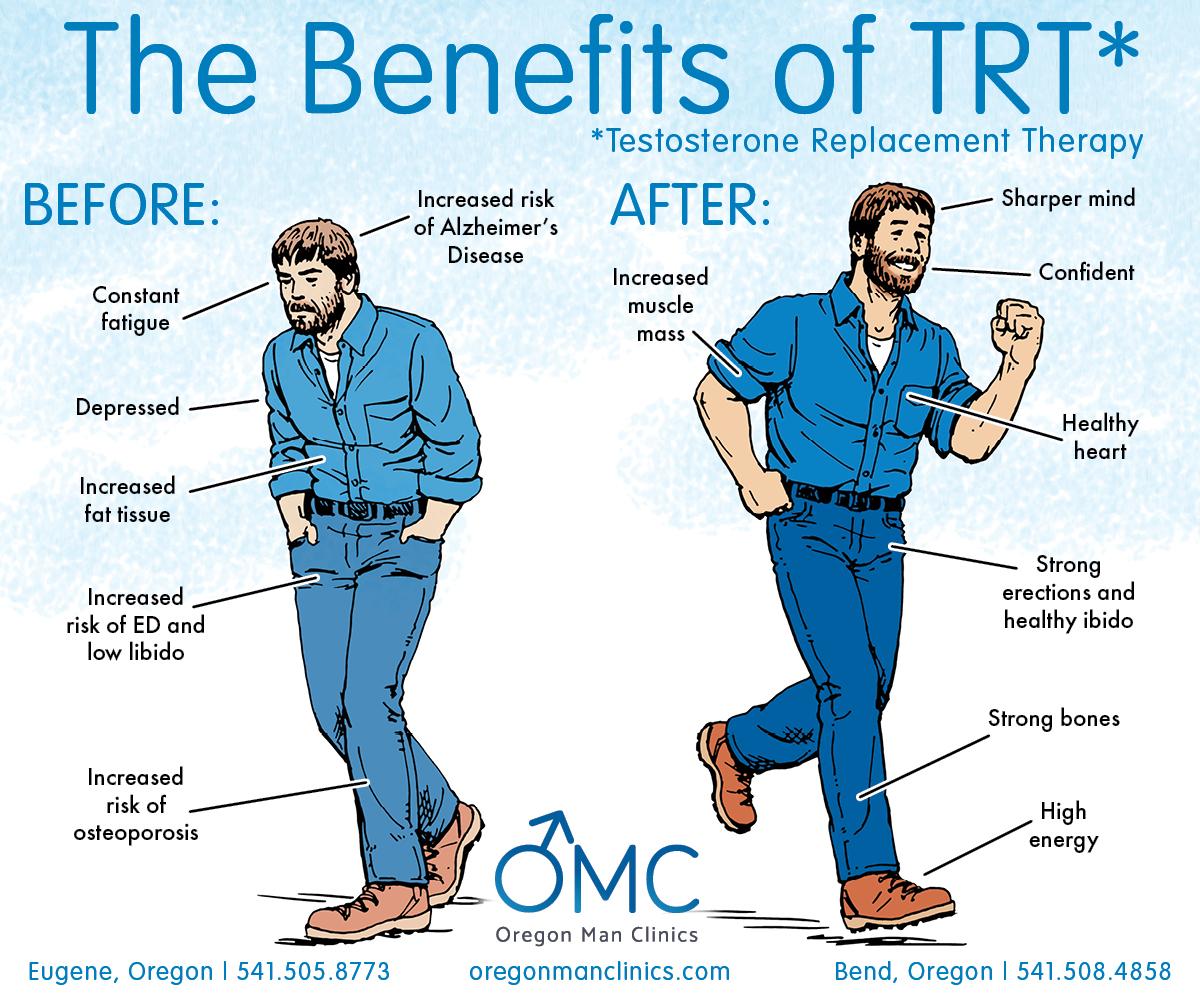
Assessing the Risks and Considerations of Hormonal Treatments
The decision to initiate hormonal treatments for type 2 diabetes, specifically testosterone therapy, necessitates a thorough assessment of potential risks. Among the most notable concerns are adverse cardiovascular effects, which may include increased blood pressure and alterations in cholesterol levels. Other considerations include the possibility of exacerbating sleep apnea, which can disrupt overall health and well-being. It is essential to weigh these risks against the perceived benefits, particularly when evaluating the therapy’s potential to improve insulin sensitivity and glycemic control.
In addition to physical health, psychological implications must also be acknowledged. Testosterone therapy can influence mood and emotional stability, with some individuals experiencing changes such as irritability or mood swings. It is crucial for healthcare providers to monitor such psychological effects closely. Before embarking on this treatment, patients should engage in a thorough discussion with their healthcare team to explore various factors, including:
- Individual health history – Previous medical conditions can influence treatment outcomes.
- Medication interactions – Assessing current medications to avoid adverse interactions.
- Long-term implications – Considering the sustainability and potential needs for ongoing therapy.
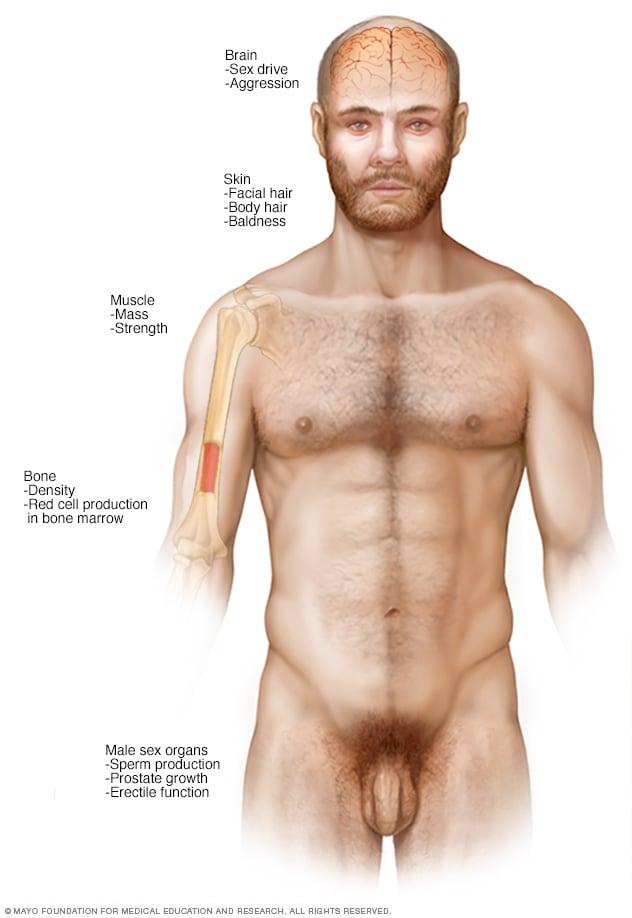
Personalizing Treatment Plans: When Testosterone Therapy is Recommended
When considering testosterone therapy for individuals with type 2 diabetes, a personalized treatment plan becomes essential. Each patient’s unique health profile, including their age, symptoms, and diabetes management history, plays a crucial role in determining if testosterone supplementation is appropriate. Key indicators that may lead a healthcare provider to recommend this therapy include:
- Low testosterone levels confirmed through blood tests
- Presence of symptoms such as fatigue, decreased libido, or muscle weakness
- Evidence of metabolic syndrome or insulin resistance
- Unmanaged blood glucose levels despite traditional diabetes treatments
Moreover, a thorough assessment is necessary to evaluate potential risks versus benefits. For instance, patients with certain conditions, such as prostate issues or severe sleep apnea, may need to tread cautiously before starting therapy. Below is a simple comparison that highlights some potential benefits and risks associated with testosterone therapy in the context of type 2 diabetes:
| Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|
| Improved insulin sensitivity | Potential cardiovascular risks |
| Increased energy levels | Hormonal imbalance |
| Enhanced muscle mass | Exacerbation of pre-existing conditions |
Monitoring and Adjusting Testosterone Levels in Diabetic Patients
Monitoring testosterone levels in diabetic patients is critical for achieving optimal therapeutic outcomes. Regular assessments allow healthcare providers to gauge whether treatment is effective, adjusting dosages as necessary. When tracking testosterone levels, consider the following key points:
- Baseline Testing: Establish initial testosterone levels to guide subsequent treatments.
- Frequency: Regular blood tests (typically every 3-6 months) to monitor hormone levels.
- Symptom Assessment: Evaluate clinical symptoms such as fatigue, mood changes, and sexual function changes, which can indicate the need for adjustment.
Adjustments to testosterone therapy should be made based on both laboratory results and patient-reported outcomes. Practitioners can utilize a systematic approach by creating a monitoring plan that includes:
| Parameter | Ideal Range | Adjustment Action |
|---|---|---|
| Total Testosterone | 300-1000 ng/dL | Increase dosage if levels are below range. |
| Free Testosterone | 5-21 ng/dL | Consider switching delivery method or adjusting dose. |
| SHBG (Sex Hormone Binding Globulin) | 10-70 nmol/L | Evaluate with endocrinology if elevated. |
Combining Lifestyle Interventions with Hormone Therapy for Optimal Results
Integrating lifestyle modifications with hormone therapy can lead to significant improvements in managing type 2 diabetes. Adopting healthier habits can not only amplify the benefits of testosterone therapy but also promote overall well-being. Consider the following lifestyle changes that complement treatment:
- Nutrition: Emphasizing a balanced diet rich in whole foods, fiber, and lean proteins can optimize testosterone levels and enhance insulin sensitivity.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise, particularly resistance training and aerobic activities, can boost testosterone and improve metabolic health.
- Sleep Hygiene: Prioritizing restorative sleep can help regulate hormones and improve energy levels.
- Stress Management: Engaging in mindfulness practices or relaxation techniques can lower cortisol levels, allowing testosterone therapy to be more effective.
To visualize the synergistic effects of combining these interventions with hormone therapy, the following table outlines potential health benefits:
| Intervention | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|
| Balanced Diet | Improved blood sugar control |
| Regular Exercise | Increased muscle mass and endurance |
| Quality Sleep | Enhanced hormonal balance |
| Stress Reduction | Lowered risk of insulin resistance |
The Future of Testosterone Therapy in Diabetes Care: Research and Innovations
Recent studies highlight the potential role of testosterone therapy as a transformative approach in managing type 2 diabetes, particularly for those experiencing symptomatic androgen deficiency. Research indicates that restoring testosterone levels can have several beneficial effects, such as:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Optimal testosterone levels may enhance the body’s ability to utilize insulin effectively, leading to better glycemic control.
- Weight Management: Testosterone therapy may assist in regulating body composition, reducing adiposity, and promoting lean muscle mass, which is crucial for metabolic health.
- Mood Enhancement: Patients often report enhanced mood and energy levels following testosterone therapy, which can have a positive impact on lifestyle changes essential for diabetes management.
Innovations in the formulation and delivery of testosterone therapy are underway, focusing on maximizing safety and efficacy. Researchers are exploring various methods, including:
- Transdermal Systems: Patches and gels offer a non-invasive approach to administering testosterone, providing controlled absorption while minimizing side effects.
- Long-acting Injectables: Extended-release formulations could reduce the frequency of administration and improve patient adherence to therapy.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Algorithms that consider genetic, hormonal, and metabolic factors are being developed to customize testosterone therapy, ensuring a more tailored approach to diabetes care.
| Benefits of Testosterone Therapy | Clinical Evidence |
|---|---|
| Increased insulin sensitivity | Studies show a significant reduction in HbA1c levels. |
| Weight loss | Clinical trials report a reduction in body fat percentage. |
| Enhanced mood and energy | Patient surveys indicate improved quality of life scores. |
Q&A
Q&A: Testosterone Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes
Q: What is testosterone therapy, and how might it relate to type 2 diabetes?
A: Testosterone therapy involves the administration of testosterone, typically through injections, patches, or gels, to individuals with low testosterone levels. Research has suggested a potential link between testosterone deficiency and insulin resistance, which is a key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. By restoring testosterone levels, the therapy may help improve insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic health.
Q: Who is a suitable candidate for testosterone therapy in the context of type 2 diabetes?
A: Suitable candidates typically include men with confirmed low testosterone levels and fully diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Healthcare providers consider factors such as age, the severity of symptoms linked to low testosterone, and individual health histories. Importantly, testosterone therapy should always be discussed with a healthcare professional to weigh the benefits against potential risks.
Q: What potential benefits does testosterone therapy offer for those with type 2 diabetes?
A: Preliminary studies have indicated that testosterone therapy may lead to improved glycemic control, enhanced insulin sensitivity, and even weight loss. Patients might experience increased energy levels, better mood, and improved physical function. However, individual responses can vary significantly.
Q: Are there risks associated with testosterone therapy for men with type 2 diabetes?
A: Yes, while testosterone therapy can offer benefits, it is not without risks. Potential side effects may include an increased risk of cardiovascular issues, prostate enlargement, sleep apnea, and other hormonal imbalances. Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is critical to manage these risks.
Q: How might lifestyle changes complement testosterone therapy for type 2 diabetes?
A: Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and weight management can enhance the effectiveness of testosterone therapy. By adopting healthier habits, patients not only improve their overall well-being but may also maximize the benefits of the therapy itself.
Q: What does recent research say about the effectiveness of testosterone therapy for treating type 2 diabetes?
A: Recent studies show promising results regarding the effectiveness of testosterone therapy in enhancing metabolic parameters in men with low testosterone and type 2 diabetes. However, research is ongoing, and there remains a need for larger, more diverse population studies to establish definitive conclusions and guidelines.
Q: How can someone begin testosterone therapy if they have type 2 diabetes?
A: The first step is to consult with a healthcare provider who will conduct a thorough evaluation, including blood tests to measure testosterone levels. If low testosterone is diagnosed alongside type 2 diabetes, the provider will discuss the potential benefits and risks of initiating therapy and outline a tailored treatment plan.
Q: In sum, what should individuals with type 2 diabetes consider when thinking about testosterone therapy?
A: Individuals with type 2 diabetes contemplating testosterone therapy should prioritize a holistic approach. Consulting a healthcare professional to understand personal health, discussing the potential benefits and risks, and exploring complementary lifestyle changes are essential steps. Balancing treatment with a proactive approach to health can lead to improved outcomes and quality of life.
In Summary
the exploration of testosterone therapy as a potential avenue for managing type 2 diabetes opens the door to new possibilities in the complex interplay of hormones and metabolic health. While research continues to unveil the nuances and implications of this treatment, it is essential for patients to consult with healthcare professionals to consider the benefits, risks, and individual circumstances. As we stand at the crossroads of science and medicine, the pursuit of innovative strategies to enhance quality of life and overall well-being remains a collective journey. Whether as a beacon of hope or a subject for further investigation, testosterone therapy invites us all to rethink conventional approaches to diabetes management in the quest for a healthier future.









