In recent years, testosterone therapy has emerged as a focal point of health discussions, offering potential benefits for many individuals grappling with hormonal imbalances. As the conversation around this treatment expands, it increasingly intersects with another crucial aspect of wellness: liver health. The liver, often dubbed the body’s silent workhorse, plays an instrumental role in metabolism, detoxification, and overall physiological balance. Yet, the relationship between testosterone therapy and liver function remains complex and somewhat controversial. This article seeks to unravel the intricate web connecting testosterone levels with liver health, shedding light on both the promises and pitfalls of therapy. By examining current research and expert insights, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview, helping readers navigate this multifaceted topic with clarity and understanding.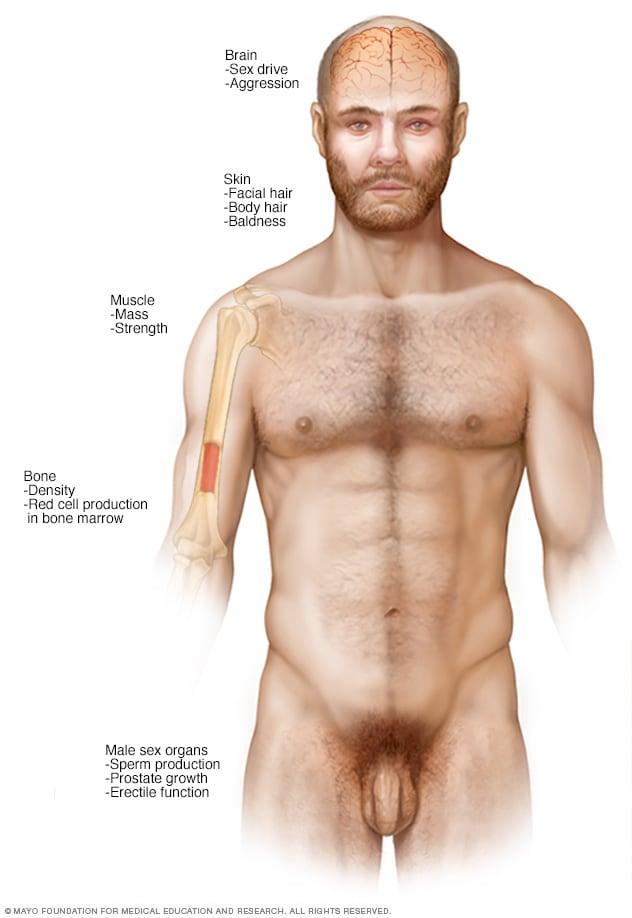
Understanding Testosterone Therapy and Its Role in Mens Health
Testosterone therapy is often explored for its potential benefits in enhancing male vitality, but its implications for liver health demand careful consideration. When administered appropriately, testosterone can positively influence various aspects of men’s health, including muscle mass, mood, and overall well-being. However, there are concerns surrounding its impact on liver function, particularly when therapy is not closely monitored or when higher doses are used. Men undergoing testosterone therapy should ensure they maintain regular check-ups to monitor liver enzymes, as fluctuations can indicate potential adverse effects.
It’s essential to understand the intricate balance between testosterone levels and liver health. For instance, some studies suggest that moderate testosterone therapy may even contribute to improved liver function in men with certain conditions such as metabolic syndrome. However, excessive testosterone can lead to complications, such as hepatic steatosis, where fat builds up in the liver. Men considering or currently on testosterone therapy might benefit from being aware of signs of liver distress, such as jaundice, abdominal pain, or unusual fatigue. Below is a table summarizing key factors related to testosterone therapy and liver health:
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Dosing | Maintain prescribed levels; avoid excessive use. |
| Monitoring | Regular liver function tests recommended. |
| Symptoms | Watch for jaundice, pain, or fatigue. |
| Consultation | Engage with healthcare providers for personalized plans. |
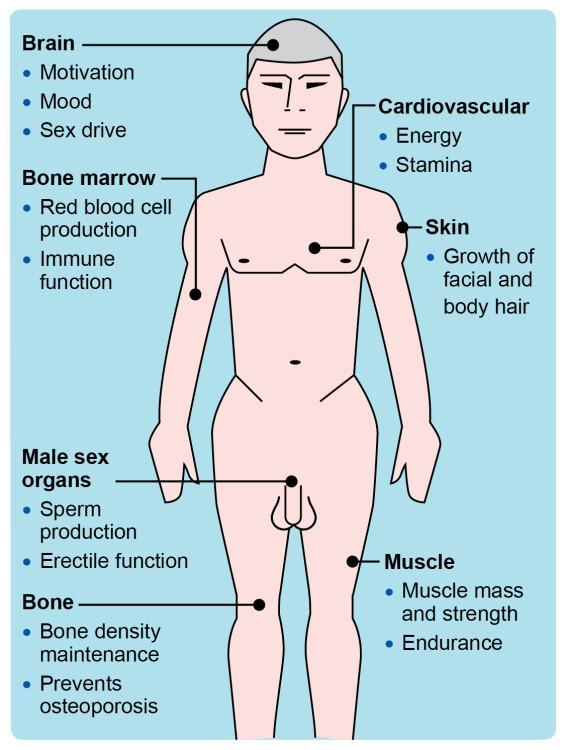
The Link Between Testosterone Levels and Liver Function
The relationship between testosterone levels and liver function is a complex yet fascinating subject. Research has indicated that testosterone plays a crucial role in the regulation of various metabolic processes in the liver. Low testosterone levels have been linked to an array of liver-related issues, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and fibrosis. This connection can be attributed to testosterone’s influence on lipid metabolism, as it reduces the accumulation of fatty deposits and enhances insulin sensitivity in liver cells. Increased awareness of this link suggests that managing testosterone levels could potentially serve as an adjunct therapy for individuals grappling with liver conditions.
Conversely, the impact of liver health on testosterone levels should not be overlooked. Liver dysfunction can lead to hormonal imbalances, causing a decrease in testosterone production. In particular, conditions such as cirrhosis disrupt the body’s ability to metabolize hormones effectively. Notably, a vicious cycle may ensue, where compromised liver function leads to lower testosterone levels, which in turn exacerbates liver issues. To illustrate the potential effects, consider the following table:
| Condition | Effect on Testosterone | Impact on Liver Health |
|---|---|---|
| Low Testosterone | Reduced levels | Increased risk of NAFLD |
| Cirrhosis | Decreased production | Exacerbated hormonal imbalances |
| Healthy Testosterone | Balanced levels | Potential for improved liver function |
Exploring the Effects of Testosterone Therapy on Liver Enzymes
Testosterone therapy has gained attention for its role in various health conditions, but its effects on liver enzymes remain an area of active research. Several studies suggest that while testosterone can influence metabolic processes, it can also lead to variations in liver enzyme levels. In some cases, individuals undergoing therapy have experienced mild elevations in enzymes such as AST (aspartate aminotransferase) and ALT (alanine aminotransferase), which are crucial markers for liver health. Monitoring these enzymes is vital, as elevated levels may indicate liver strain or damage.
Healthcare providers typically recommend regular blood tests to evaluate liver function throughout testosterone therapy. This precaution ensures any potential adverse effects are identified early, allowing for adjustments in treatment as necessary. The relationship between testosterone and liver enzymes can be influenced by several factors, including:
- Dosage of testosterone: Higher doses may correlate with increased enzyme levels.
- Duration of therapy: Long-term therapy requires careful monitoring.
- Individual health status: Pre-existing liver conditions can alter enzyme responses.
Understanding these nuances can help guide safe and effective use of testosterone therapy while safeguarding liver health. Here’s a brief overview of potential enzyme changes associated with therapy:
| Parameter | Typical Range | During Testosterone Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| AST | 10 – 40 U/L | Potential increase of 5 - 15 U/L |
| ALT | 7 – 56 U/L | Potential increase of 10 – 20 U/L |
| ALP | 44 – 147 U/L | No significant changes expected |
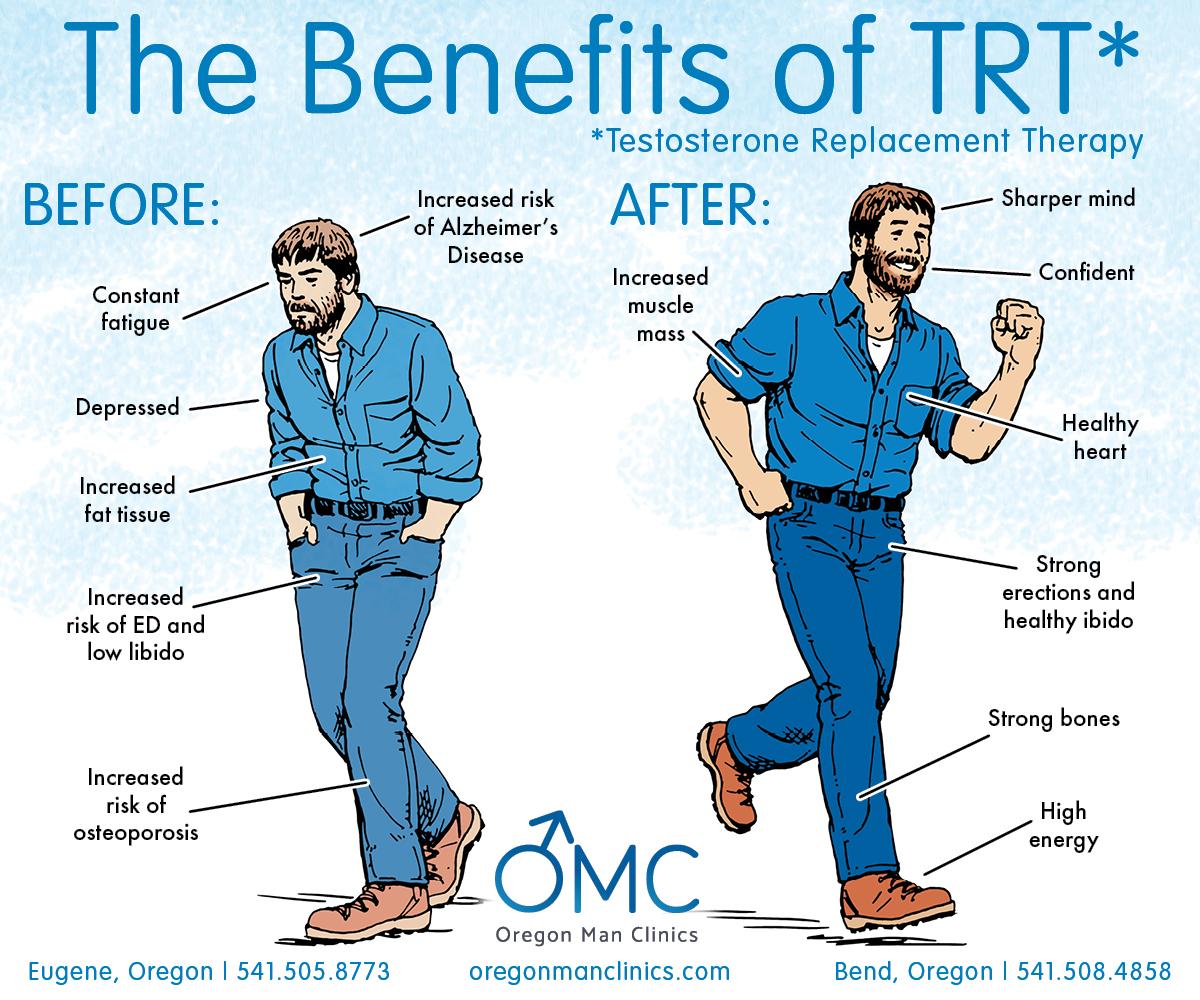
Risks and Benefits of Testosterone Treatment for Liver Health
Testosterone treatment can have both positive and negative impacts on liver health. On the beneficial side, when testosterone levels are restored to normal ranges, it can potentially enhance liver function by improving metabolic processes and reducing visceral fat. This can lead to a decrease in liver-related complications for individuals with conditions such as fatty liver disease. Moreover, testosterone may assist in maintaining muscle mass, which is crucial for overall metabolic health and can aid in weight management, further benefitting the liver.
Conversely, there are risks associated with testosterone therapy that cannot be overlooked. Elevated testosterone levels can lead to liver toxicity, particularly when administered in high doses or through improper methods. Potential risks include:
- Increased cholesterol levels, promoting fatty deposits in the liver
- Potential for liver tumors with long-term use
- Adverse reactions in individuals with pre-existing liver conditions
Monitoring liver function through regular blood tests is crucial for anyone undergoing testosterone therapy. Awareness and management of these risks can help doctors provide safer treatment options and maximize the therapeutic benefits to liver health.
Monitoring Liver Function During Testosterone Therapy
Regular assessments of liver function are imperative for individuals undergoing testosterone therapy, as accumulating data suggests potential impact on liver health. While testosterone itself is not inherently toxic to the liver, the way it’s administered—especially through oral preparations—can pose risks. Clinicians typically recommend monitoring liver enzymes, providing a clearer picture of hepatic function and any potential side effects. It’s also essential to evaluate a patient’s medical history and any pre-existing liver conditions to tailor the therapy appropriately.
Monitoring parameters often include:
- ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase): Elevated levels can indicate liver inflammation.
- AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase): A crucial marker for liver injury.
- Bilirubin: Elevated bilirubin can signal liver dysfunction.
- Albumin: Lower levels may suggest chronic liver disease.
| Test | Normal Range | Indication of Issues |
|---|---|---|
| ALT | 7-56 U/L | Possible liver damage |
| AST | 10-40 U/L | Possible liver or muscle issues |
| Bilirubin | 0.1-1.2 mg/dL | Potential liver dysfunction |
| Albumin | 3.5-5.0 g/dL | Concern for chronic liver disease |
Incorporating these assessments into routine follow-ups ensures any adverse reactions are caught early. Patients should remain vigilant for symptoms indicating liver stress, such as jaundice, fatigue, or abdominal discomfort, and report these to their healthcare provider promptly. By emphasizing preventive care and monitoring, the goal is not only to optimize testosterone therapy but also to safeguard overall liver health, ensuring a balanced approach to hormone management.
Lifestyle Strategies to Support Liver Health While on Therapy
Supporting liver health during testosterone therapy involves a holistic approach that integrates dietary considerations, physical activity, and mindfulness practices. Prioritize a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and healthy fats to mitigate potential side effects. Focus on incorporating foods such as:
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens
- Fatty fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines
- Nuts and seeds: Walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds
- Fruit: Berries are particularly beneficial
In addition to nutrition, regular exercise can enhance liver function and overall well-being. Engaging in a mix of aerobic and resistance training increases blood flow and helps regulate hormones. Consider implementing a weekly routine that includes:
| Activity | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Walking or jogging | 3-5 times a week |
| Strength training | 2-3 times a week |
| Yoga or Pilates | 2 times a week |
consider mindfulness practices like meditation and deep breathing exercises to reduce stress, as chronic stress can negatively impact liver function. Integrating these lifestyle strategies can substantially support your liver health while undergoing therapy, promoting both physical and mental well-being.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals for Safe Testosterone Management
For individuals considering testosterone therapy, consulting healthcare professionals is paramount to ensure a tailored approach that prioritizes safety and efficacy. An experienced endocrinologist or urologist can conduct comprehensive assessments to evaluate hormonal balance and liver health. Key considerations during this consultation should include:
- Medical history evaluation – Assess pre-existing liver conditions and overall health.
- Laboratory tests – Regular monitoring of liver enzymes and testosterone levels.
- Risk assessment – Identifying factors that may increase the risk of liver complications.
Health professionals can provide guidance on safe administration, including dosage adjustments and potential need for lifestyle changes. Furthermore, understanding the implications of testosterone therapy on liver function is crucial, particularly in the case of oral administration, which can exert more strain on the liver. A common practice is to transition to intramuscular injections or transdermal applications to mitigate risks. Explore the following table for a comparison of testosterone administration methods and their impact on liver health:
| Administration Method | Liver Impact | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Oral Tablets | Higher risk of liver strain | Daily |
| Intramuscular Injections | Lower risk; direct into bloodstream | Weekly/Monthly |
| Transdermal Patches | Minimal liver impact; systemic absorption | Daily |
Q&A
Q&A: Navigating the Intersection of Testosterone Therapy and Liver Health
Q1: What is testosterone therapy, and why do people undergo it?
A1: Testosterone therapy involves the administration of testosterone to address hormonal deficiencies, often due to aging, medical conditions, or specific health challenges. Individuals may seek this therapy to alleviate symptoms such as fatigue, low libido, reduced muscle mass, or mood changes, aiming to restore vitality and improve overall quality of life.
Q2: How does testosterone therapy impact liver health?
A2: The relationship between testosterone therapy and liver health is complex. While testosterone itself is not predominantly processed by the liver, some forms of testosterone, especially when taken orally, can exert strain on liver function. It’s crucial to monitor liver enzymes and overall health during therapy, as certain side effects may arise.
Q3: Are there specific risks associated with testosterone therapy for the liver?
A3: Yes, particularly with oral testosterone formulations, there may be an increased risk of liver toxicity and conditions such as cholestasis, where bile flow is obstructed. However, injectable and transdermal (skin patch or gel) forms are generally considered safer for the liver. Regular monitoring is essential to catch any potential liver issues early.
Q4: How can individuals who are on testosterone therapy monitor their liver health?
A4: Regular check-ups are key! Healthcare providers typically recommend baseline liver function tests before starting therapy and subsequent tests at regular intervals. It’s important for individuals to discuss any symptoms, such as jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), unexplained fatigue, or abdominal pain, as these could indicate liver distress.
Q5: What lifestyle changes can support liver health while undergoing testosterone therapy?
A5: Adopting a liver-friendly lifestyle can significantly contribute to overall health. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, staying hydrated, limiting alcohol intake, avoiding illicit drugs, and engaging in regular physical activity. These practices support liver function and can complement the benefits of testosterone therapy.
Q6: Who should avoid testosterone therapy due to liver concerns?
A6: Individuals with pre-existing liver conditions, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis, may be at higher risk and should approach testosterone therapy cautiously. It’s essential for these patients to undergo comprehensive evaluations and consultations with healthcare providers specializing in hormone therapy and liver health.
Q7: What is the takeaway for those considering testosterone therapy regarding liver health?
A7: The key takeaway is that while testosterone therapy can offer significant benefits for those with hormonal imbalances, it is paramount to remain vigilant about liver health. Open communication with healthcare providers, regular liver function screenings, and healthy lifestyle choices can help ensure that therapy proceeds safely and effectively. Always approach treatment decisions with informed caution and professional guidance.
Wrapping Up
the intricate dance between testosterone therapy and liver health showcases the complexity of human physiology. As we’ve explored, while testosterone therapy can offer significant benefits to those with hormonal imbalances, it also warrants a cautious approach, particularly concerning liver function. With ongoing research shedding light on this multifaceted relationship, it remains essential for individuals considering or currently undergoing testosterone therapy to engage in open discussions with healthcare providers. By prioritizing informed decisions and regular monitoring, one can navigate the path of hormone therapy with a mindful awareness of its effects on overall health. As we continue to unravel the nuances of our bodies, striking a balance between treatment and well-being remains the key to a vibrant life.










