Navigating the Intersection of Hormones and Heart Health: Testosterone Therapy and Cholesterol Levels
In a world where health narratives constantly evolve, the relationship between hormones and heart health continues to garner attention. Testosterone therapy, often hailed for its potential benefits in energy, mood, and muscle mass, has ignited discussions that extend beyond mere vitality. One pivotal question emerges: how does this therapy influence cholesterol levels, a critical component of cardiovascular health? As men and women increasingly turn to testosterone treatments, understanding the nuanced interplay between testosterone and cholesterol becomes essential. In this article, we delve into the latest research, exploring the effects of testosterone therapy on cholesterol profiles and the broader implications for heart health, aiming to shed light on this complex hormonal equation.
Understanding the Connection Between Testosterone Therapy and Cholesterol
Testosterone therapy, often used to elevate low hormone levels, has been found to have a complex relationship with cholesterol levels. On one hand, restoring testosterone levels can positively influence lipid profiles by potentially increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. HDL is known as the “good” cholesterol because it helps to remove other forms of cholesterol from the bloodstream, potentially lowering the risk of heart disease. Conversely, some studies indicate that testosterone therapy may also lead to increased low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, which is commonly referred to as “bad” cholesterol due to its association with plaque buildup in arteries.
Understanding this dichotomy is essential for healthcare providers and patients alike. Factors that can influence how testosterone therapy impacts cholesterol include:
- Type of testosterone administered: Different formulations can have varying effects on lipid profiles.
- Dosage and administration method: Higher doses and certain delivery methods (e.g., injections vs. patches) may lead to differing outcomes.
- Individual health factors: Pre-existing health conditions, metabolic factors, and lifestyle choices can all affect cholesterol responses.
| Testosterone Therapy Impact | Cholesterol Type | Typical Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Testosterone Replacement | HDL | Potential Increase |
| Testosterone Replacement | LDL | Potential Increase |
The Biological Impact of Testosterone on Lipid Profiles
The relationship between testosterone levels and lipid profiles is complex and multifaceted. Research indicates that testosterone therapy can significantly influence cholesterol levels, with various effects depending on the individual’s baseline levels and overall health. Studies suggest that testosterone might lead to a decrease in LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, commonly known as “bad” cholesterol, while simultaneously supporting an increase in HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, or ”good” cholesterol. This shift can potentially translate into a lower risk for cardiovascular diseases, making it essential to monitor lipid profiles during treatment.
Moreover, the impact of testosterone on lipid metabolism is believed to be mediated through several biological pathways, including:
- Enhancement of fat oxidation: Testosterone can stimulate the breakdown of fats, aiding in maintaining a healthier lipid profile.
- Regulation of lipoprotein receptors: Testosterone may improve the uptake of lipoproteins by cells, reducing circulating LDL levels.
- Influence on liver function: The hormone has been shown to modulate liver enzymes that are crucial for cholesterol synthesis and clearance.
| Cholesterol Type | Effect of Testosterone Therapy |
|---|---|
| LDL | Decreased |
| HDL | Increased |
| Total Cholesterol | Variable Effects |
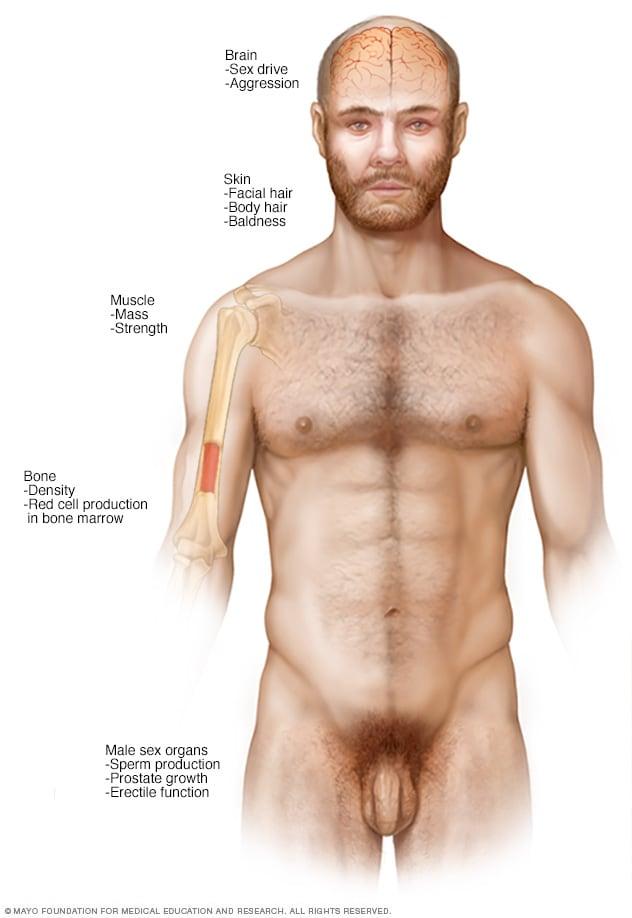
Evaluating the Effects of Testosterone Replacement on Cholesterol Levels
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) has become a topic of considerable interest, particularly regarding its impact on cardiovascular health markers, such as cholesterol levels. A growing body of evidence suggests that TRT can influence lipid profiles in men facing low testosterone. Some studies indicate an improvement in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often referred to as the “good” cholesterol, which is linked to reduced cardiovascular risk factors. However, the effect on low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides remains more complex and requires careful consideration.
In light of these findings, it’s essential for healthcare professionals to conduct comprehensive assessments that balance the benefits and risks of testosterone therapy. Monitoring lipid profiles before and during TRT can guide treatment decisions. Here are some key points to consider:
- Patient individualization: The effects of TRT can vary significantly among individuals.
- Regular monitoring: Periodic lipid profiling is advisable to track changes over time.
- Contextual analysis: Other factors such as age, diet, and comorbidities play a role in cholesterol management.
| Cholesterol Type | Effect of TRT |
|---|---|
| HDL | Potential increase |
| LDL | Variable effects |
| Triglycerides | Mixed results |
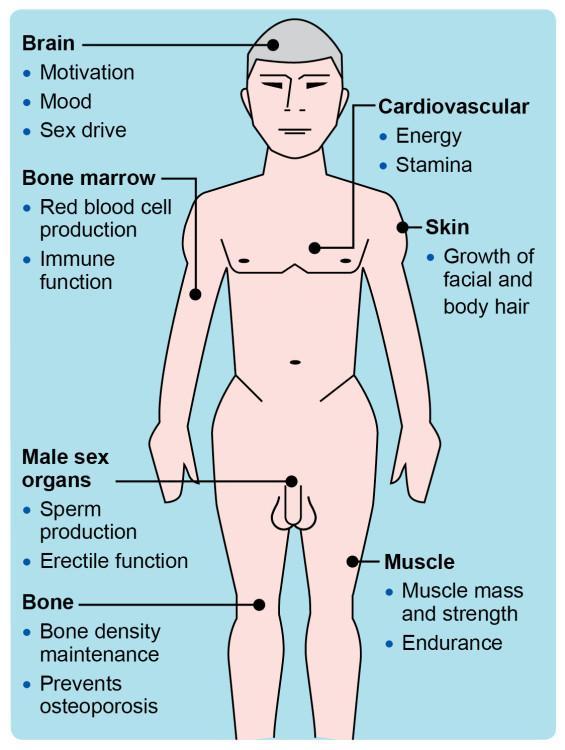
Assessing Potential Risks and Benefits of Testosterone Therapy
Testosterone therapy has gained attention for its potential impact on a variety of health markers, particularly cholesterol levels. While some studies suggest that testosterone can improve lipid profiles by increasing HDL (the “good” cholesterol) and decreasing LDL (the “bad” cholesterol), it is essential to recognize that results can vary widely among individuals. Factors such as age, pre-existing health conditions, and lifestyle choices play a crucial role in determining whether testosterone therapy will yield beneficial or detrimental effects on lipid levels.
It’s important to weigh both the risks and benefits before starting testosterone therapy. Potential benefits include:
- Enhanced energy levels
- Improved mood and cognitive function
- Increased muscle mass and strength
- Better sexual function
However, possible risks may include:
- Increased risk of cardiovascular events
- Potential negative effects on cholesterol levels
- Interaction with other medications
Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for personalized advice and monitoring to help navigate these complexities, ensuring that therapy aligns with overall health goals.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Healthy Cholesterol During Treatment
Making strategic lifestyle changes can significantly bolster the effectiveness of testosterone therapy in managing cholesterol levels. Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine is one of the most impactful modifications. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises and strength training at least five times a week. In addition to exercise, it’s important to focus on your diet. Consider incorporating foods that are known to lower bad cholesterol (LDL) and enhance good cholesterol (HDL), such as:
- Oats and Whole Grains – Rich in soluble fiber, which helps reduce cholesterol levels.
- Fatty Fish – Omega-3 fatty acids lower triglycerides and promote heart health.
- Nuts – Especially walnuts and almonds, which are heart-healthy.
- Fruits and Vegetables – Packed with antioxidants that can protect against heart disease.
Additionally, it’s crucial to manage stress levels, as chronic stress can negatively impact cholesterol and overall cardiovascular health. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Monitoring alcohol intake and quitting smoking are also pivotal steps. Studies show that eliminating tobacco and reducing alcohol consumption can enhance your cholesterol profile. For a clearer understanding, here’s a brief comparison of how smoking and alcohol affect cholesterol:
| Factor | Effect on Cholesterol |
|---|---|
| Smoking | Increases LDL; lowers HDL |
| Alcohol (in moderation) | May help raise HDL levels |
Clinical Guidelines for Monitoring Cholesterol in Testosterone Therapy Patients
Monitoring cholesterol levels in patients undergoing testosterone therapy is essential, as changes in lipid profiles can occur during treatment. Healthcare providers should adhere to the following guidelines to ensure proper management:
- Initial Assessment: Perform a baseline lipid profile before initiating testosterone therapy.
- Regular Monitoring: Schedule follow-up lipid panels at 3, 6, and 12 months post-therapy initiation, and annually thereafter.
- Symptom Assessment: Evaluate any new symptoms of cardiovascular issues, such as chest pain or shortness of breath.
- Individualized Approach: Consider patient risk factors, including family history, pre-existing conditions, and lifestyle.
If lipid levels are altered significantly, practitioners should reassess the testosterone dosage or treatment plan. It’s crucial to understand the relationship between testosterone and cholesterol, as testosterone can impact fats in the blood differently among individuals. The table below summarizes optimal cholesterol levels for patient management:
| Lipid Type | Optimal Level (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Total Cholesterol | < 200 |
| LDL (Bad Cholesterol) | < 100 |
| HDL (Good Cholesterol) | ≥ 60 |
| Triglycerides | < 150 |
Future Research Directions: Exploring the Testosterone-Cholesterol Relationship
The intricate relationship between testosterone and cholesterol presents numerous avenues for future exploration. Investigating the mechanisms of action whereby testosterone influences lipid profiles could shed light on conflicting studies regarding its effects on cholesterol levels. Prospective research could focus on:
- Longitudinal studies assessing the long-term impacts of testosterone therapy on both total and LDL cholesterol.
- Biomarker identification that could predict individual responses to testosterone therapy.
- Population-based research targeting diverse demographics to evaluate genetic factors that may regulate cholesterol metabolism in relation to testosterone.
Furthermore, it is imperative to explore the potential benefits of testosterone therapy in managing dyslipidemia, particularly among populations experiencing metabolic syndrome or cardiovascular diseases. Analysis could encompass:
| Research Area | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|
| Effects on HDL levels | Understanding how testosterone may support cardiovascular health. |
| Interaction with statin therapy | Evaluating synergistic effects on cholesterol management. |
| Gender-based differences | Identifying distinct responses to testosterone therapy between males and females. |
These investigations could yield critical insights, paving the way for personalized treatment strategies that optimize both testosterone levels and lipid profiles in various patient populations.
Q&A
Title: Testosterone Therapy and Cholesterol Levels: What You Need to Know
Q1: What is testosterone therapy, and why is it used?
A1: Testosterone therapy involves the administration of testosterone to individuals with low testosterone levels, a condition often referred to as hypogonadism. This therapy aims to restore hormone levels to normal, enhancing energy, mood, libido, muscle mass, and overall quality of life.
Q2: How does testosterone therapy impact cholesterol levels?
A2: Testosterone therapy’s relationship with cholesterol is complex. Some studies suggest that testosterone may positively influence the lipid profile by lowering levels of LDL cholesterol (often labeled as “bad” cholesterol) and possibly raising HDL cholesterol (“good” cholesterol). However, individual responses can vary significantly.
Q3: Are there risks associated with testosterone therapy concerning cholesterol?
A3: Yes, while some may experience improvements in their cholesterol levels, others may face complications. There have been reports linking testosterone therapy with increased levels of hematocrit (the proportion of blood volume that is occupied by red blood cells), which could potentially lead to cardiovascular issues. It’s essential to monitor cholesterol levels and overall health regularly during therapy.
Q4: Should individuals with high cholesterol consider testosterone therapy?
A4: It’s essential for individuals with high cholesterol to consult with their healthcare provider. If low testosterone levels are diagnosed, the benefits of testosterone therapy must be weighed against the potential risks, especially regarding cholesterol and heart health. Personal medical history and associated health conditions should be considered before starting therapy.
Q5: What lifestyle changes can complement testosterone therapy in managing cholesterol levels?
A5: Alongside testosterone therapy, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can significantly improve cholesterol levels. This includes a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding tobacco use. These behaviors can enhance the effectiveness of therapy and contribute to better overall health.
Q6: How should patients be monitored during testosterone therapy?
A6: Regular monitoring is crucial. Patients should have their testosterone levels checked periodically, along with comprehensive lipid panels to assess cholesterol levels. Healthcare providers may also conduct other evaluations, such as checking blood pressure and hematocrit levels, to ensure that the therapy is not leading to adverse effects.
Q7: Is there a one-size-fits-all approach to testosterone therapy?
A7: Absolutely not. Testosterone therapy should be individualized based on a person’s unique medical history, symptoms, and cholesterol levels. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals can help tailor the approach, ensuring safety and efficacy throughout the therapy.
Q8: What future research is needed in this area?
A8: Future research should focus on long-term outcomes of testosterone therapy on cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health. Large-scale clinical trials could help clarify the relationship between testosterone levels and lipid profiles, providing clearer guidelines for practitioners and patients alike.
Q9: Where can patients find reliable information about testosterone therapy and cholesterol?
A9: Patients can consult reputable sources such as endocrinology or cardiology associations, peer-reviewed medical journals, and their healthcare providers for accurate information. It is vital to sift through the plethora of online resources and stick to those that are evidence-based and scientifically validated.
Conclusion: Testosterone therapy can offer significant benefits for those with low testosterone levels, but its effects on cholesterol can vary. Engaging in informed discussions with medical professionals, coupled with an understanding of one’s health, is crucial in navigating this complex relationship.
In Summary
In the intricate dance of hormones and health, testosterone therapy emerges as a pivotal player influencing not only vitality but also cholesterol levels. As we navigate the complexities of this treatment, it’s essential to weigh both its benefits and potential risks. While the allure of increased energy and improved mood can be enticing, the interplay with cholesterol presents a nuanced landscape that warrants careful consideration.
For those contemplating testosterone therapy, an informed dialogue with a healthcare provider is imperative—equipped with the knowledge of how this intervention may alter lipid profiles and overall heart health. The journey towards optimal wellness is a personal one, shaped by individual circumstances and medical histories.
Ultimately, as science continues to unravel the connections between testosterone and cholesterol, we are reminded of the delicate balance our bodies maintain. By staying informed and proactive, we can navigate this terrain with confidence, making choices that fortify our health for the long term. Here’s to embracing our well-being with both caution and curiosity, as we explore the profound effects of hormones on our lives.










